A Guide to 404 Error Pages

There are inevitably times when a website does not work as intended. When people try to visit it, they get the 404 error message instead. But what is a 404 error, and why is it important for a website? This article will explain this important component of every website.

Discover how at OpenReplay.com.
Many people have encountered 404 errors occasionally. This could have a strong impact on a website’s UX and SEO, increasing the bounce rate, damaging quality links, and creating indexing issues, both internal and external. However, it’s an unknown problem that only users know about, so it’s important to regularly check SEO audits to find this error.
The usual trigger for a 404 message is the content of a website that has been moved to a different URL or removed already. However, other reasons could also trigger the error message.
The 404 error page could be useful for spotting and resolving problems. Or, it can also be a source of frustration that makes people leave the website. For website owners, creating user-friendly 404 pages that state what the visitor needs to do next in a clear manner is paramount. It could, otherwise, drive prospective customers away and leave the website with a negative impression.
Furthermore, website owners should understand what the 404 error pages mean. Also known as 404 not found, the error page is an error message designed to appear when a website fails to load. The pages are specifically related to DNS problems.
This means the browser cannot find any website matching what was typed. There are two reasons for this. First, it’s possible that the website that used to load is no longer operating under the same address. It could have moved to a new address or been taken down. Another possibility is that a website visitor entered the wrong URL address.
Difference between Soft 404 and Hard 404 Error
Recently, Google confirmed that expired e-commerce platform products will be deemed “soft 404s”. What does this mean for a website?
A soft 404 is not an official message sent to the server. Instead, it is deemed a label. Google assigns a soft 404 label to pages within its index if it feels that the page resembles a standard 404 response code.
Google will get alerts on unusual behavior even if it seems like a hard 404 error because the soft 404 pages, at times, will continue to relay 200 success codes. The soft 404 label notes that while a success code may be sent, something is not right.
A hard 404 is an HTTP status or response code. Response codes communicate with the server about a page’s loading status. The codes, which are numerically presented, allow the server to know what kind of issue the page is experiencing and the reason for it. Specifically, a hard 404 indicates that the page does not exist anymore and will not be returning to the website anytime soon.
Common Examples of 404 Error Pages
Look at some common design examples of 404 error pages for better understanding.
Below is an example of a 404 error page from Google.
 Here’s another example of a 404 error page from Openreplay.
Here’s another example of a 404 error page from Openreplay.
 Example of a 404 error page from Tesla.
Example of a 404 error page from Tesla.
Main Causes of 404 Error Pages
There are several causes why 404 Error Pages occur. The following are the most common causes.
Web Page Deletion
When trying to access a page and finding that it does not exist anymore, you could have reached a dead end. One of the most common reasons for the message to appear is that the page was deleted. The website may, however, redirect you to another relevant page.
Editing the Page in Progress
Sometimes, a page may appear to be dead end, but it’s simply because someone is currently editing it or working on it. This occurs usually when the page content is revised or updated. When someone updates the page, it’s important to publish and make it available for public access when the task is completed to prevent users from encountering a 404 error.
Wrong Page Redirection
URLs should be changed for several reasons. One is that you’re doing a website migration. If this is the case, then it would be a good idea to change the URLs to reflect the new structure of the website. Moreover, it’s also a good idea to consolidate web pages, which could also require changing the URLs.
Another reason a URL should be changed is SEO optimization to boost search engine rankings. In some instances, a web page may have been moved, but the URL was not redirected to the new location, which could result in a 404 error even if the page was not deleted.
Mistyping the URL
Sometimes, it’s as simple as mistyping a URL. Before getting worried or making phone calls, make sure to double-check the spelling of the URL. Remember that typos are a common mistake, which could lead you to think you have an issue with your website when it works fine.
Major Impacts of 404 Error Pages
The 404 is not always a bad thing. If a page is removed and not returned, it’s perfectly fine to show website visitors that it no longer exists. URLs coming with 404 errors will be removed from the Google index after some time. Let’s check out how a 404 error impacts a website.
SEO Performance
Due to continuous 404 errors, a particular website page’s ranking will be down. The page will not be ranked, which could hurt sales. For search engines to rank a page, they first need to index it.
However, if the search engine encounters a 404 error, it will realize that the page does not exist; thus, it will not index or rank it. This means that users will not be able to discover the page through a search engine search. Search engines will not rank pages with 404 errors; thus, these pages will have fewer eligible pages to display on SERPs.
Bad User Experience
Good user experience is the gateway to website traffic. Now, if you have a website that stops the users’ attempts to see products and services because of the 404 error message, users will undoubtedly stop trying and turn to the competition instead. Furthermore, search engines will take note of high bounce rates and lower the web page’s ranking.
How to Identify 404 Error Pages?
How do you determine if you have 404 error pages? Clicking on every link to find out if it leads to a “page not found” error message could be time-consuming and tedious. Try these instead.
Google Search Console
The Google Search Console or GSC is a Google tool that gives you a website report on the Google SERP’s performance. This includes a page indexing report displaying URLs with “soft” and “hard” 404 errors, among other things. GSC could take up to a week to display data from a newly added website.
- Go to the “Indexing” section on the left-hand menu in Google Search Console and click on Pages.
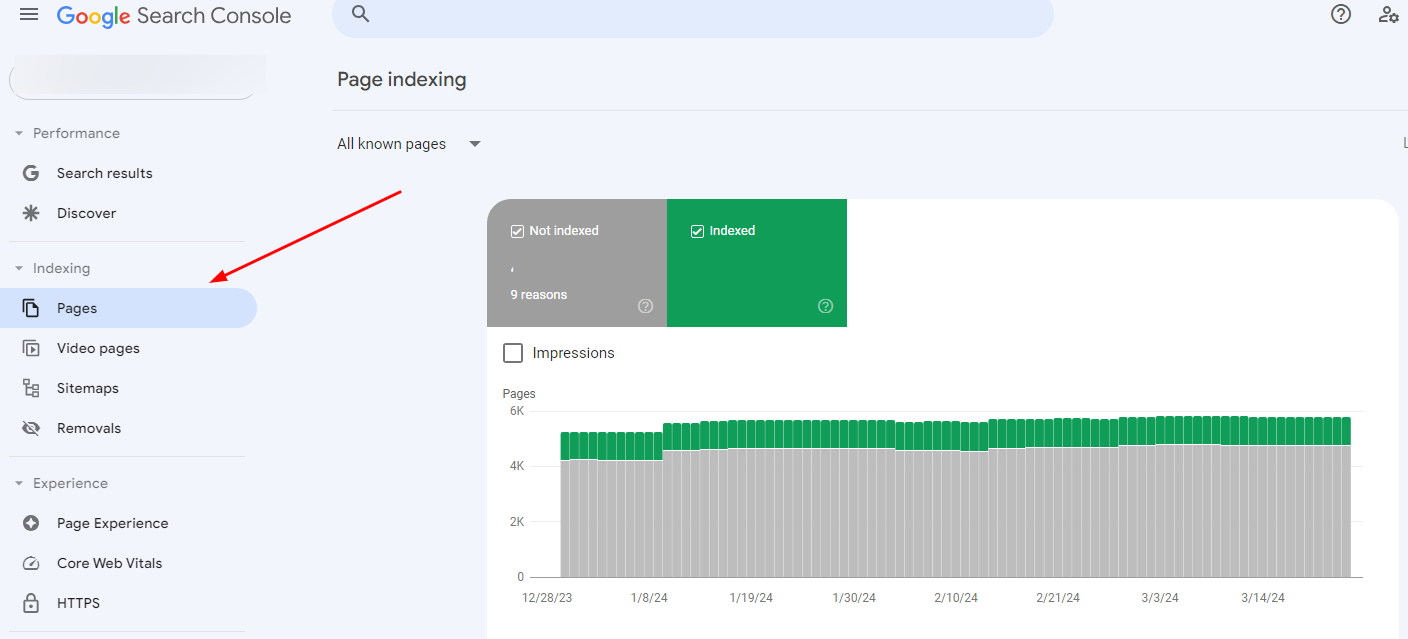
- Scroll down below and look at Not Found(404) in the Why Why pages aren’t indexed section.
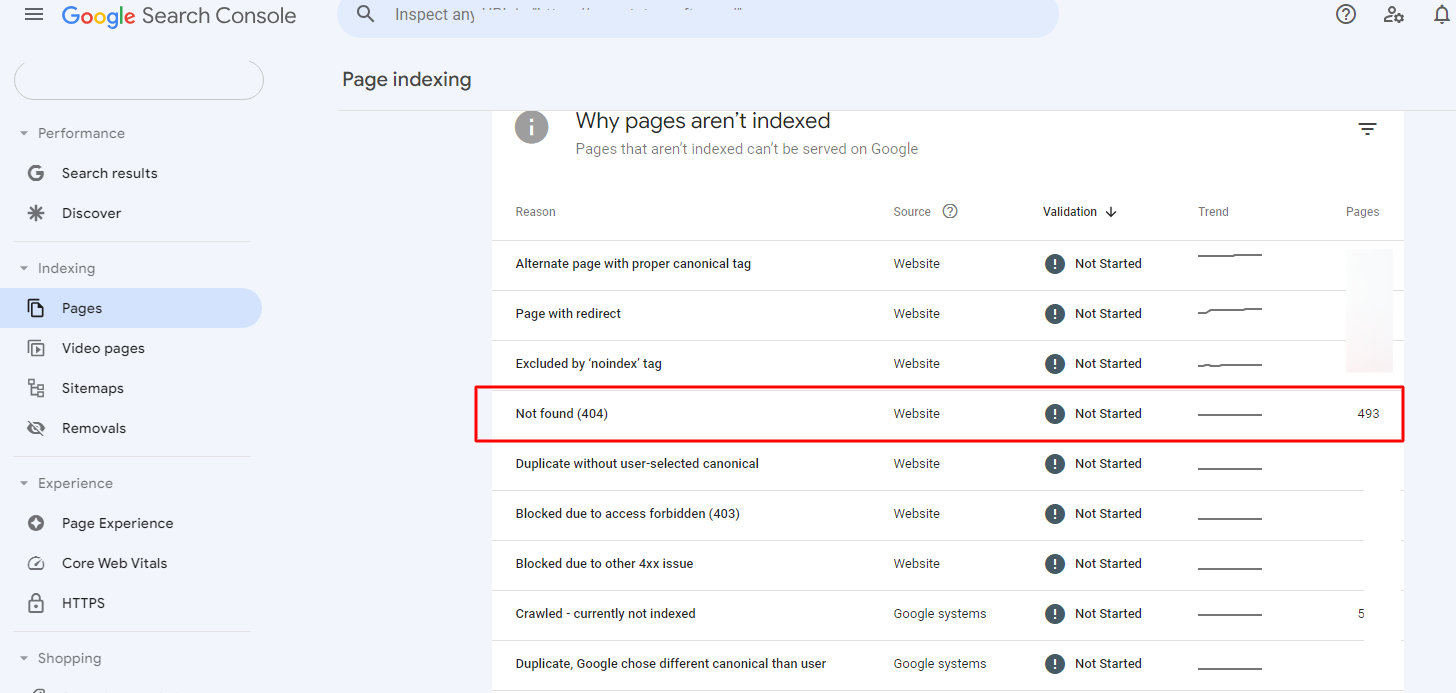
- Click on Not Found (404), and you’ll get the list of all the pages with the error.
WordPress Plugins
Websites with WordPress as a CMS can easily be downloaded from the list of WordPress plugins like Broken Link Checker. Those plugins can help in detecting 404 errors. Most of these solutions let you redirect your users to the correct URL or redirect them.
 Most of the plugins have a built-in 404 error page since there is a default template structure built on WordPress to display not found or 404 pages. Automatically, WordPress will display the 404 built-in page if the Not Found error happens.
Most of the plugins have a built-in 404 error page since there is a default template structure built on WordPress to display not found or 404 pages. Automatically, WordPress will display the 404 built-in page if the Not Found error happens.
SEO Tools
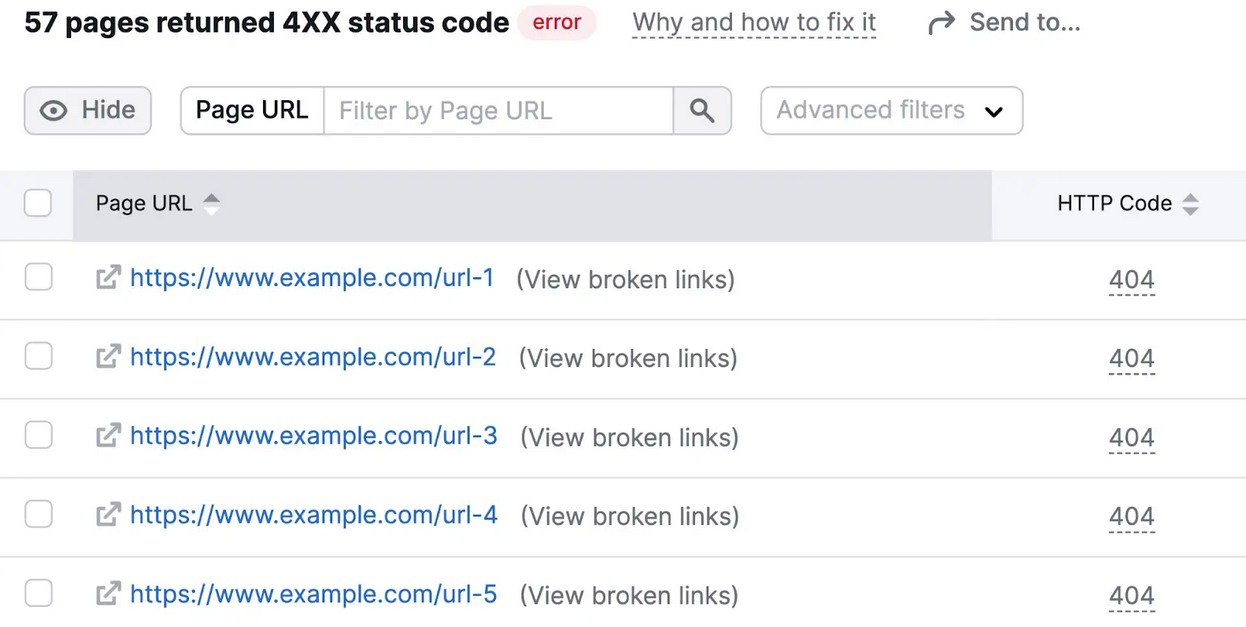
There are several SEO tools, such as Semrush, Screaming Frog, and others to help you identify 404 error pages. Semrush, in particular, is a tool that can detect more than 140 technical website problems, including 404 errors. Moreover, the tool suggests solutions to fix the issues found.
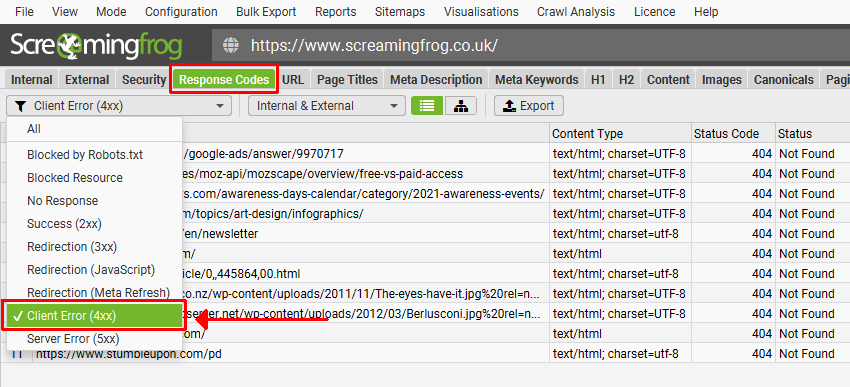
 Screaming Frog is another SEO tool that helps find crawl errors. It’s a desktop application that crawls the website and analyzes different SEO factors, including meta tags, titles, links, headers, etc.
Screaming Frog is another SEO tool that helps find crawl errors. It’s a desktop application that crawls the website and analyzes different SEO factors, including meta tags, titles, links, headers, etc.
How to Fix 404 Error Pages
After knowing about how to identify the 404 error pages using different tools available in the market. Let’s find out how to fix the 404 error pages.
Check the URL
An error may have been made whether you manually entered the URL address or via a link. Therefore, you should consider checking the website’s specified path. Moreover, it’s also possible that you or another person mistyped something.
Besides spelling mistakes, forward slashes may have been left out or misplaced. Nevertheless, keep in mind that this could be checked only with “clean” URLs since they contain unreadable words rather than incomprehensible letters, symbols, abbreviations, and numbers.
An example of a wrong or mistyped URL showing a 404 status code.
https://www.openreplay.com/prodct.html
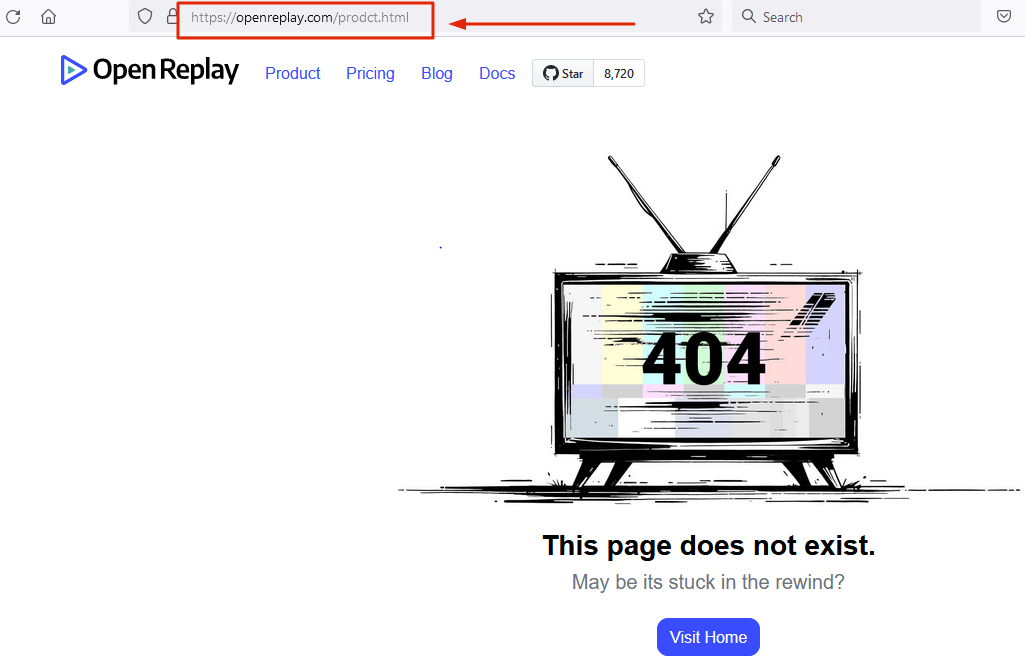 The Correct URL should be
The Correct URL should be https://www.openreplay.com/product.html
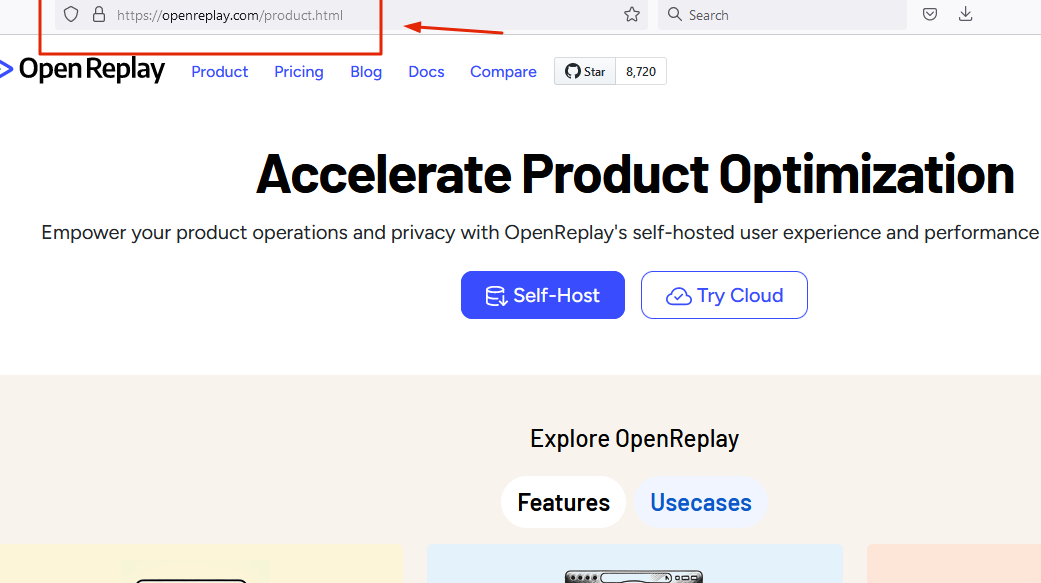
Redirecting the URL that Causes the 404 Error
Another way to prevent users from landing on a non-existent page is to set up a redirect that takes them somewhere else automatically. This is an ideal solution if you have moved the contents of the page from the original URL to a different one.
For example, if you’ve moved your page earlier found at https://www.demo.com/page1 to https://www.demo.com/page/page1 then you need to configure 301 redirect protocol using .htaccess file using command Redirect 301 /page1 https://www.demo.com/page/page1.
Moreover, a redirect can take users to a new page location without updating all the instances of your website link.
When you redirect, it ensures that external links referring to a missing page will not generate a 404 error. There are instances when you might also set up redirects in anticipation of user errors.
Clear the Browser’s Cache
If you can open the page on another device, for instance, you can reach the URL from your phone but not from a desktop. Clearing the cache on your tablet’s browser could do the trick.
Moreover, it would be a good idea to clear the browser cookies, or at least those that are involved with the website in question in case cache clearing does not work. The browser may also have cached an outdated version which could result in a 404 error, so clearing the cache could help.
Remove the URL that Causes the 404 Error from the Website
Remove the URL that causes the 404 error if you no longer need it. This way, users would not be able to click it on the website and risk getting detected to a 404 error. The pages could be edited to remove the links throwing 404 errors.
Conclusion
Having an error of 404 pages is not necessarily a bad thing. However, you should be aware of which pages they are to take action to fix unwanted errors that could impact the user experience. Again, not all 404 redirects are bad.
When used correctly, these redirects could be valuable to a website because they could keep more users on the website, which in turn drives more conversions. The important thing to keep in mind is to monitor the 404 redirect errors via Google Analytics and Google Search Console. These will inform you why users are experiencing errors.
Gain control over your UX
See how users are using your site as if you were sitting next to them, learn and iterate faster with OpenReplay. — the open-source session replay tool for developers. Self-host it in minutes, and have complete control over your customer data. Check our GitHub repo and join the thousands of developers in our community.



