Chrome Extensions for Beginners -- Part 2: Practice

In this part, we will create a Pomodoro timer extension using the APIs we learned about in part 1. Styling will be done using CSS. The complete code for this project can be found on GitHub.
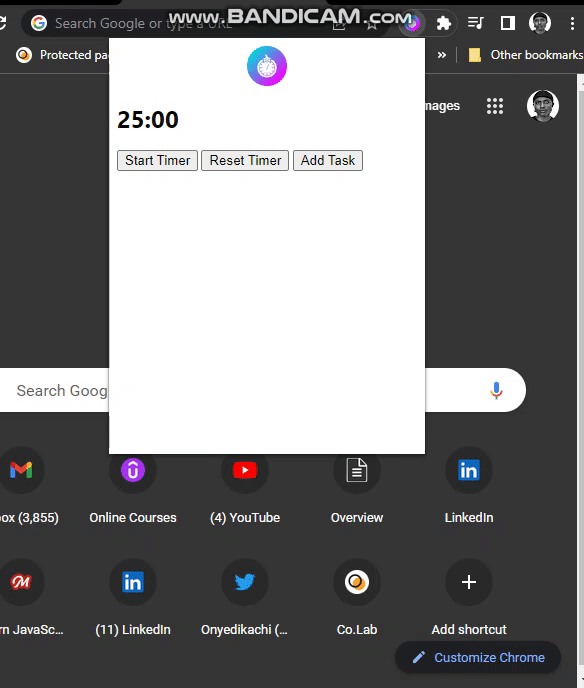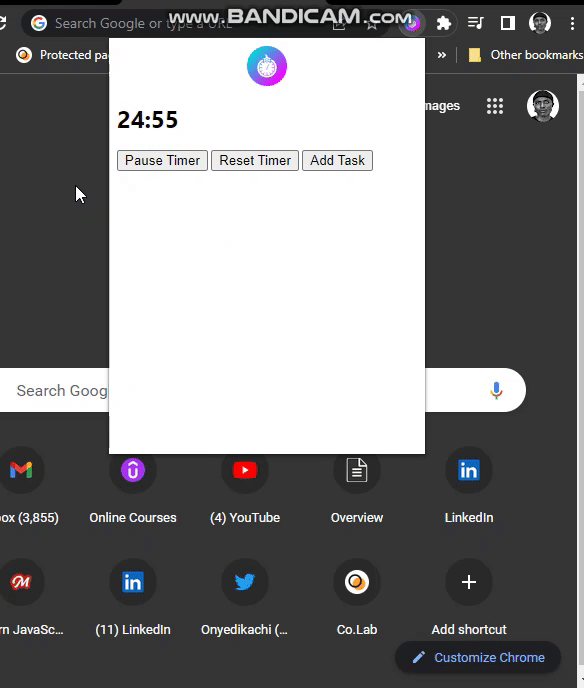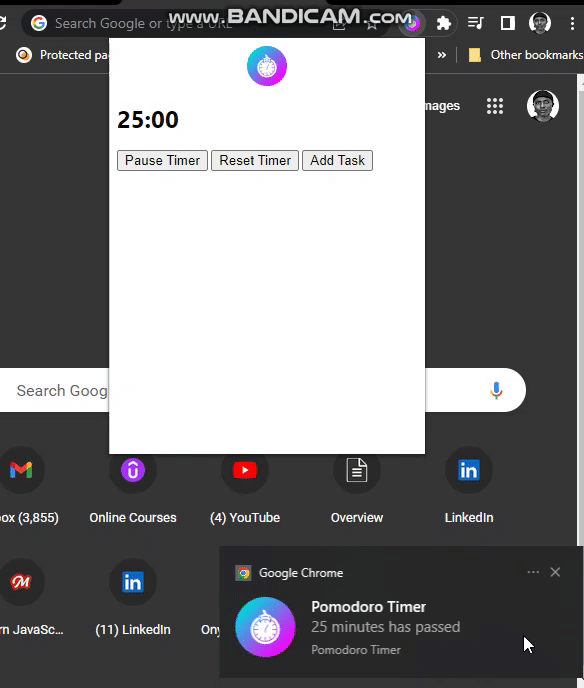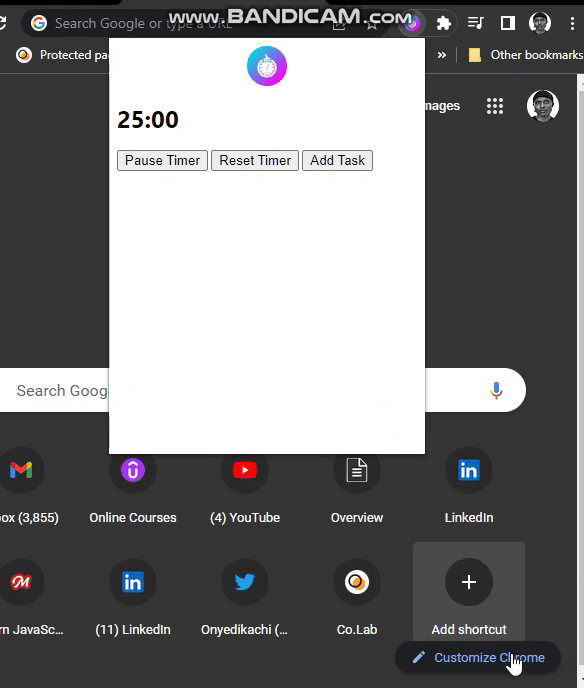
PROJECT DEMO:
Manifest and Popup
As you know by now, when building extensions, the first file you create is the manifest file.
Create a new manifest.json file.
📦 Chrome-Extension-Series
┣ 🎨 icon.png
┣ 📄 manifest.json{
"manifest_version": 3,
"name": "Pomodoro Timer",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Assists you to focus and get things done",
"icons": {
"16": "icon.png",
"48": "icon.png",
"128": "icon.png"
},
"action": {
"default_icon": "icon.png",
"default_title": "Pomodoro Timer",
"default_popup": "popup/popup.html"
}
}Now we have our extension set, let’s create the popup page. The popup.html file is placed inside the popup folder to add structure to our project.
📦 Chrome-Extension-Series
┣ 🎨 icon.png
┣ 📄 manifest.json
┣ 📂 popup
┃ ┣ 📄 popup.html <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./popup.css">
<title>Pomodoro Timer</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">
<img src="../icon.png">
</div>
<h1>00:00</h1>
<button>Start Timer</button>
<button>Add Task</button>
<div>
<input type="text">
<input type="button" value="X">
</div>
</body>
<script src="popup.js"></script>
</html>In the preceding code, the structure of our popup page is defined. It is linked to pop.css for styling and pop.js for interactivity.
Let’s add some styling and create the popup.css file our popup.html is linked to.
📦 Chrome-Extension-Series
┣ 🎨 icon.png
┣ 📄 manifest.json
┣ 📂 popup
┣ 📄 popup.css body {
height: 400px;
width: 300px;
}
.header {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
height: 40px;
}Reload the extension page on the browser and click on the popup, popup.html is displayed.
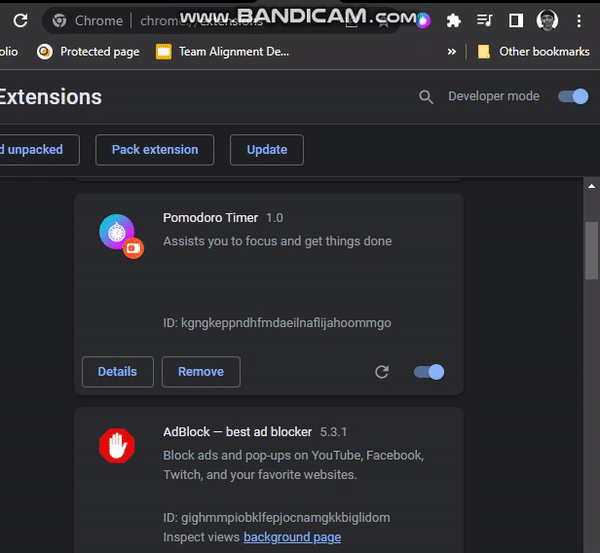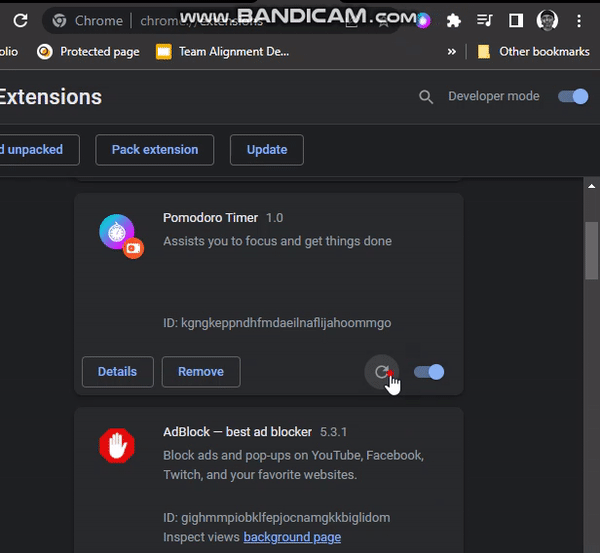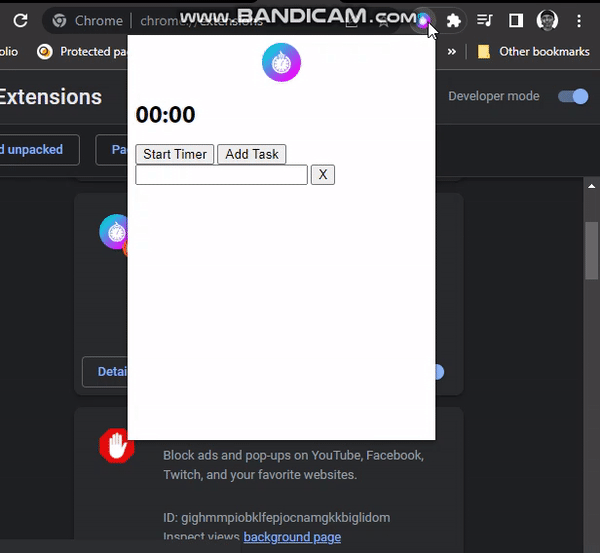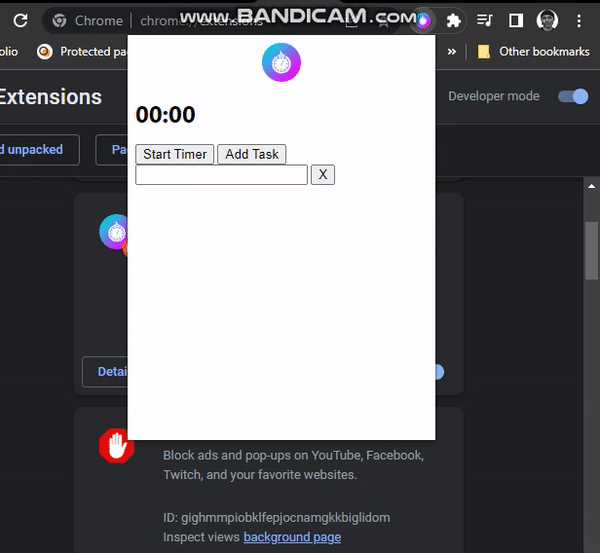
Task list feature
The task list feature will enable us to add and delete tasks.
Adding Tasks
In popup.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./popup.css">
<title>Pomodoro Timer</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="header">
<img src="../icon.png">
</div>
<h1>00:00</h1>
<button>Start Timer</button>
<button id="add-task-btn">Add Task</button>
+ <div id="task-container">
<input type="text">
<input type="button" value="X">
+ </div>
</body>
<script src="popup.js"></script>
</html>In popup.js
📦 Chrome-Extension-Series
┣ 🎨 icon.png
┣ 📄 manifest.json
┣ 📂 popup
┣ 📄 popup.css
┣ 📄 popup.jsconst addTaskBtn = document.getElementById('add-task-btn')
addTaskBtn.addEventListener('click', () => addTask())
function addTask() {
const taskRow = document.createElement('div')
// Create text input
const text = document.createElement('input')
text.type = 'text'
text.placeholder = 'Enter a task..'
// Create delete button
const deleteBtn = document.createElement('input')
deleteBtn.type = 'button'
deleteBtn.value = 'X'
// append input elements to taskRow
taskRow.appendChild(text)
taskRow.appendChild(deleteBtn)
// append taskRow to taskContainer
const taskContainer = document.getElementById('task-container')
taskContainer.appendChild(taskRow)
}In the preceding code, we select the Add Task button via its id, add a click event listener, and a callback function that adds a new task to the UI.
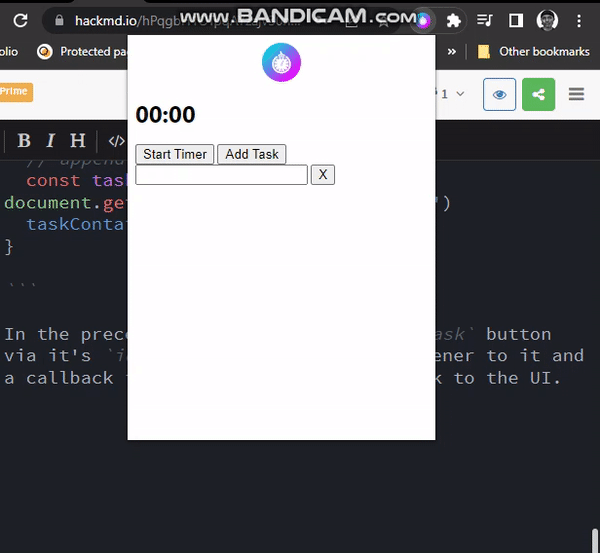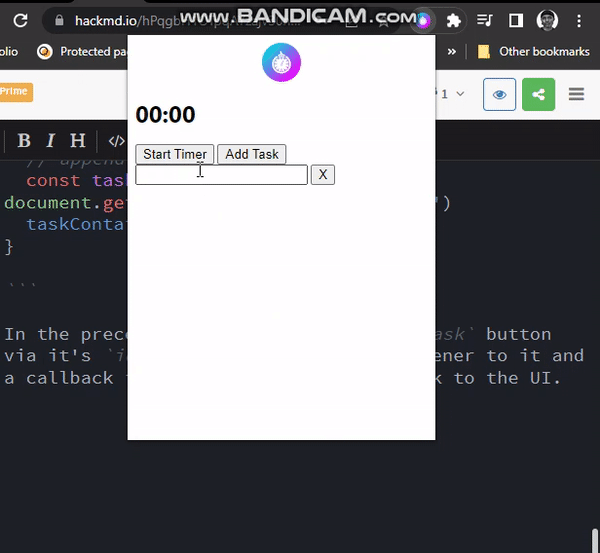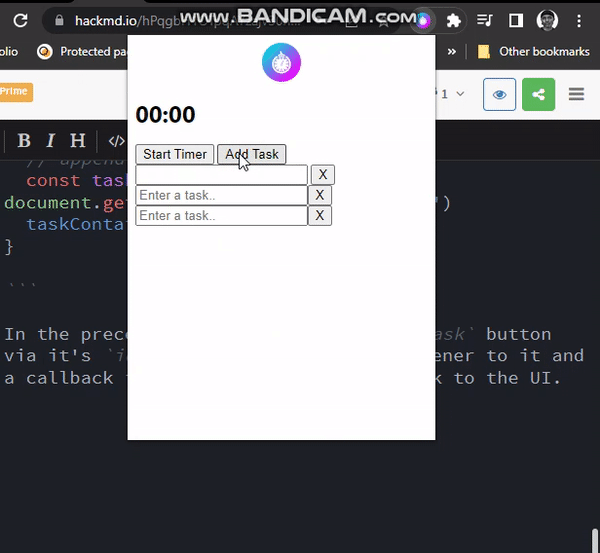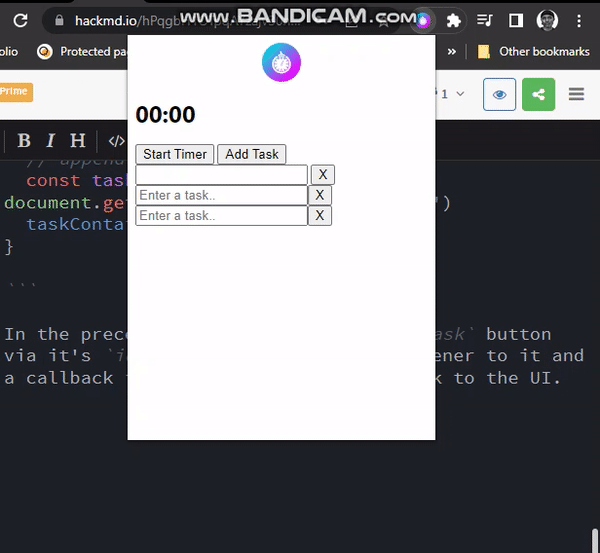
Deleting Tasks
In popup.js
- const addTaskBtn = document.getElementById('add-task-btn')
addTaskBtn.addEventListener('click', () => addTask())
- function addTask() {
const taskRow = document.createElement('div')
// Create text input
- const text = document.createElement('input')
text.type = 'text'
text.placeholder = 'Enter a task..'
// Create delete button
- const deleteBtn = document.createElement('input')
deleteBtn.type = 'button'
deleteBtn.value = 'X'
// append input elements to taskRow
taskRow.appendChild(text)
taskRow.appendChild(deleteBtn)
// append taskRow to taskContainer
- const taskContainer = document.getElementById('task-container')
taskContainer.appendChild(taskRow)
}// array to store tasks
let tasks = []
const addTaskBtn = document.getElementById('add-task-btn')
addTaskBtn.addEventListener('click', () => addTask())
// render tasks
function renderTask(taskNum) {
const taskRow = document.createElement('div')
// Create text input
const text = document.createElement('input')
text.type = 'text'
text.placeholder = 'Enter a task..'
//Set and track input values of tasks in the array
text.value = tasks[taskNum]
text.addEventListener('change', () => {
tasks[tasksNum] = text.value
})
// Create delete button
const deleteBtn = document.createElement('input')
deleteBtn.type = 'button'
deleteBtn.value = 'X'
// delete task
deleteBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
deleteTask(taskNum)
})
// append input elements to taskRow
taskRow.appendChild(text)
taskRow.appendChild(deleteBtn)
// append taskRow to taskContainer
const taskContainer = document.getElementById('task-container')
taskContainer.appendChild(taskRow)
}
function addTask() {
const tasksNum = tasks.length
// add tasks to array
tasks.push('')
renderTask(tasksNum)
}
// delete and re-render tasks after mutation
function deleteTask(tasksNum) {
tasks.splice(tasksNum, 1)
renderTasks()
}
function renderTasks() {
const taskContainer = document.getElementById('task-container')
taskContainer.textContent = ''
tasks.forEach((taskText, tasksNum) => {
renderTask(tasksNum)
})
}We have made major changes in the popup.js file in the preceding code. Let’s understand what’s happening:
- Basically, we are adding and deleting tasks
- An array(
tasks) is created to allow us to store tasks - The
rendTask()function creates a new task and renders it on the DOM(document object model) when theAdd Taskbutton is clicked. - The
addTask()function is the event handler for theAdd Taskbutton - The
deleteTask()function deletes tasks when the delete task button(X) is clicked. - The
renderTasks()function updates the task array whenever a task is deleted—i.e., it re-renders the UI.
Now, if we check our extension, we can add and delete tasks, but the data is not persistent—we need to implement storage.
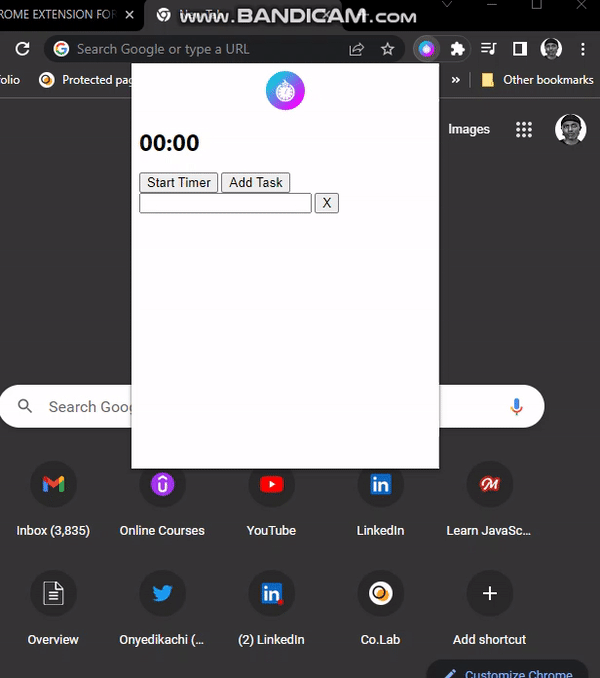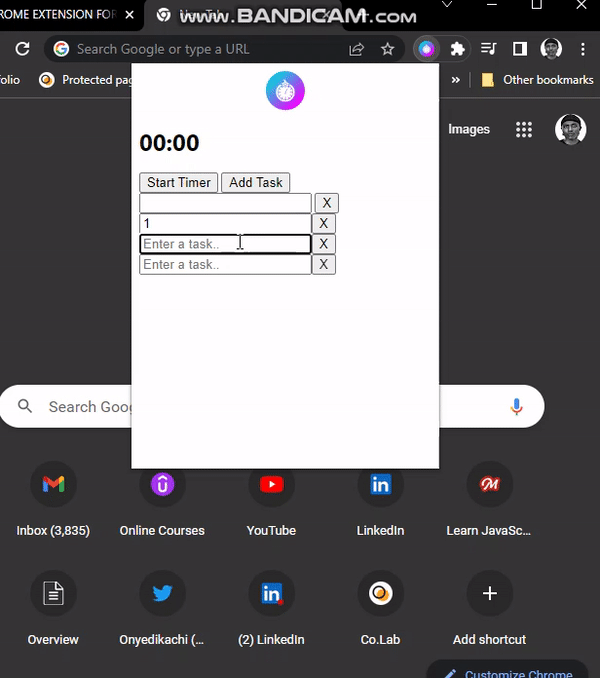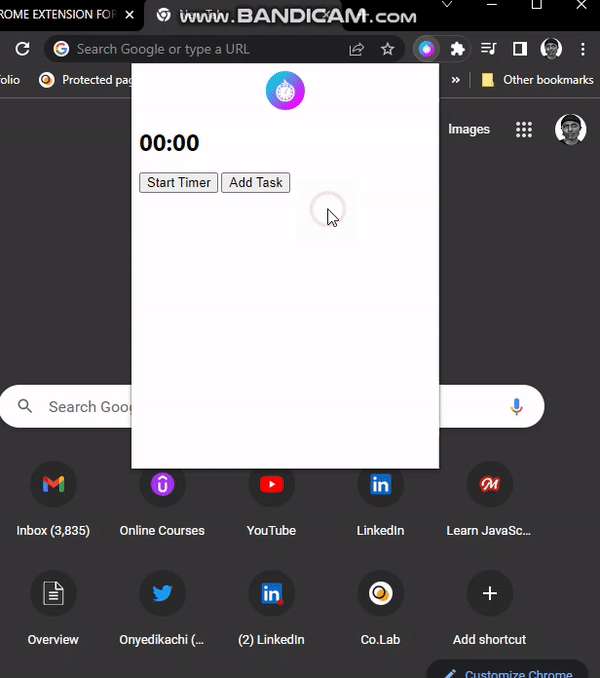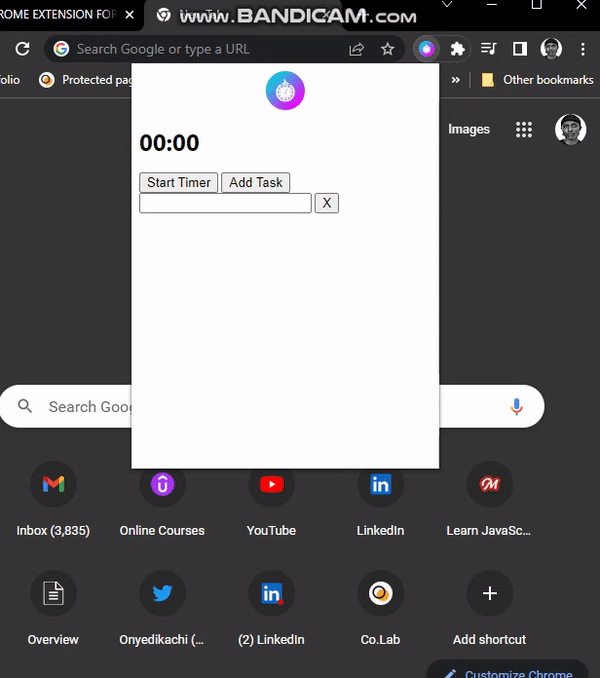
Storing Tasks
First, we have set the required permissions to use the storage API in manifest.json.
{
"manifest_version": 3,
"name": "Pomodoro Timer",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Assists you to focus and get things done",
"icons": {
"16": "icon.png",
"48": "icon.png",
"128": "icon.png"
},
"action": {
"default_icon": "icon.png",
"default_title": "Pomodoro Timer",
"default_popup": "popup/popup.html"
},
+ "permissions": ["storage"]
}In popup.js
// array to store tasks
let tasks = []
const addTaskBtn = document.getElementById('add-task-btn')
addTaskBtn.addEventListener('click', () => addTask())
// set default storage value for the tasks
chrome.storage.sync.get(['tasks'], (res) => {
tasks = res.tasks ? res.tasks : []
renderTasks()
})
// save tasks
function saveTasks() {
chrome.storage.sync.set({
tasks: tasks,
})
}
// render tasks
function renderTask(taskNum) {
const taskRow = document.createElement('div')
// Create text input
const text = document.createElement('input')
text.type = 'text'
text.placeholder = 'Enter a task..'
//Set and track input values of tasks in the array
text.value = tasks[taskNum]
text.addEventListener('change', () => {
tasks[taskNum] = text.value
// call saveTask whenever a value changes
saveTasks()
})
....
function addTask() {
const tasksNum = tasks.length
// add tasks to array
tasks.push('')
renderTask(tasksNum)
saveTasks()
}
// delete and re-render tasks after mutation
function deleteTask(tasksNum) {
tasks.splice(tasksNum, 1)
renderTasks()
saveTasks()
}We use Chrome’s storage API in the preceding code to store our extension data.
- The default data for the extension is initially set to an empty array if there are no tasks in the task array to render.
- The
saveTasks()function stores ourtaskarray in the storage API. - In
renderTask(), whenever a task is added or removed, it is saved viasaveTasks(), and the same goes foraddTask()anddeleteTask().
The task feature is complete; we can delete, add, and store tasks.

Timer feature
The timer feature will require us to create a background script and use alarms and notifications to notify the user when the timer is up.
Start And Pause Timer
Let’s set the required permissions in manifest.json.
{
"manifest_version": 3,
"name": "Pomodoro Timer",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Assists you to focus and get things done",
"icons": {
"16": "icon.png",
"48": "icon.png",
"128": "icon.png"
},
"action": {
"default_icon": "icon.png",
"default_title": "Pomodoro Timer",
"default_popup": "popup/popup.html"
},
+ "permissions": ["storage", "alarms", "notifications"],
+ "background": {
"service_worker": "background.js"
}
}Create the background.js file for our background script.
📦 Chrome-Extension-Series
┣ 🎨 icon.png
┣ 📄 manifest.json
┣ 📂 popup
┣ 📄 popup.css
┣ 📄 popup.js
┣ 📄 background.js// create an alarm to notify user when time is up
chrome.alarms.create("pomodoroTimer", {
periodInMinutes: 1 / 60
})
// alarm listener
chrome.alarms.onAlarm.addListener((alarm) => {
if (alarm.name === "pomodoroTimer") {
chrome.storage.local.get(["timer", "isRunning"], (res) => {
if (res.isRunning) {
let timer = res.timer + 1
console.log(timer)
chrome.storage.local.set({
timer,
})
}
})
}
})
// storage to set and track timer variables on load
chrome.storage.local.get(["timer", "isRunning"], (res) => {
chrome.storage.local.set({
timer: "timer" in res ? res.timer : 0,
isRunning: "isRunning" in res ? res.isRunning : false,
})
})In popup.js
// array to store tasks
let tasks = []
// Start Timer Button
+ const startTimerBtn = document.getElementById("start-timer-btn");
startTimerBtn.addEventListener("click", () => {
chrome.storage.local.get(["isRunning"], (res) => {
chrome.storage.local.set({
isRunning: !res.isRunning,
}, () => {
startTimerBtn.textContent = !res.isRunning ? "Pause Timer" : "Start Timer"
})
})
})In the preceding code:
- We set an alarm that is triggered when the
Start Timerbutton is clicked. - The
timerandisRunningvariables are used to track time and the state of the timer, they are stored as initial app data in storage. - We listen(
onAlarm.addListener) to alarm and incrementtimerwhenisRunningistrue, thentimeris logged to the console. - Finally, in
popup.js, we listen for theclickevent on theStart Timerbutton and get the currentisRunningvalue. If the current value istrue,it is set tofalse,and the timer is paused; if it isfalse,it is set to true to reset the timer.
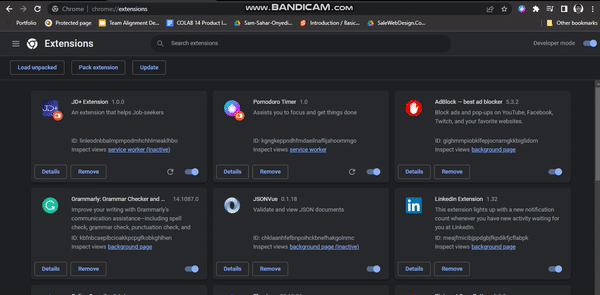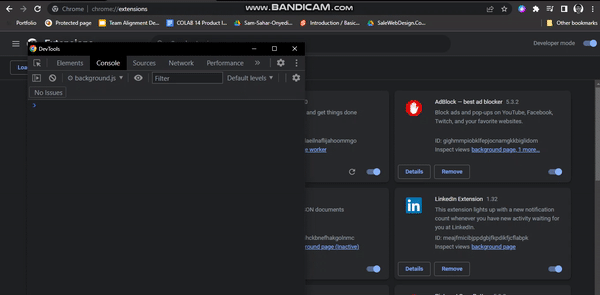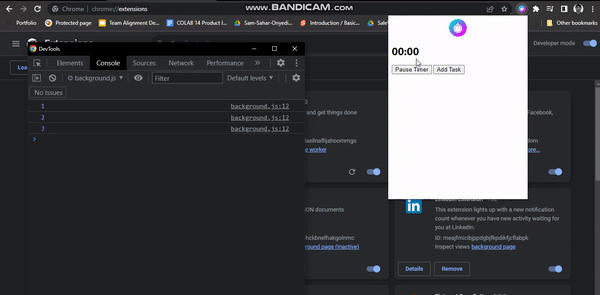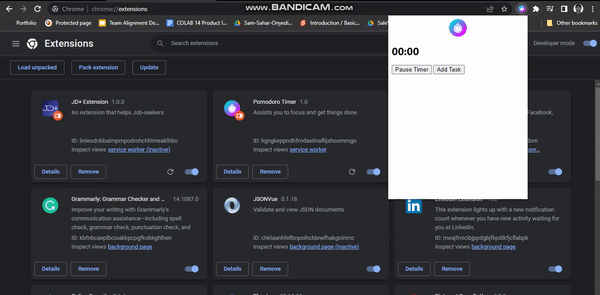
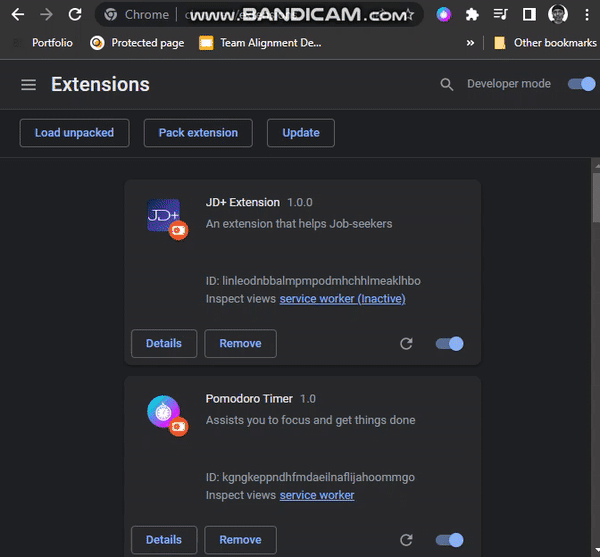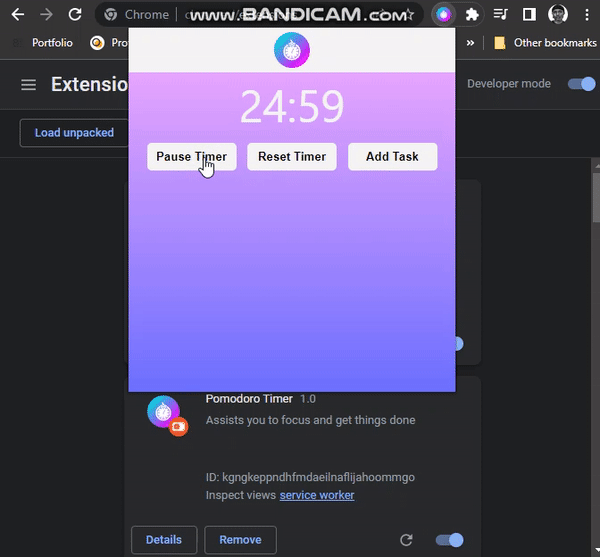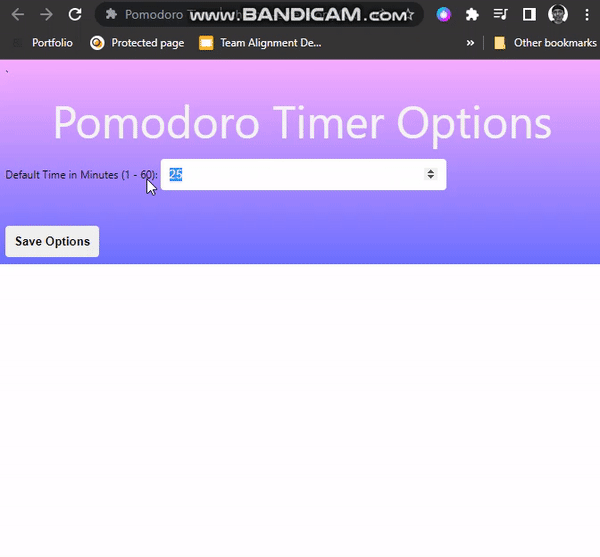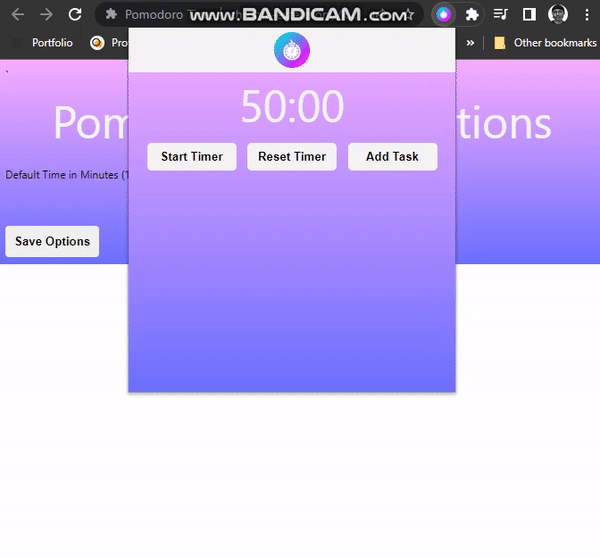
Reset Timer
Now, let’s work on the reset timer functionality. Create the markup for the reset button popup.html.
<body>
<div class="header">
<img src="../icon.png">
</div>
<h1>00:00</h1>
<button id="start-timer-btn">Start Timer</button>
+ <button id="reset-timer-btn">Reset Timer</button>
<button id="add-task-btn">Add Task</button>
<div id="task-container">
<input type="text">
<input type="button" value="X">
</div>
</body>In popup.js
// Reset Timer Button
const resetTimerBtn = document.getElementById("reset-timer-btn")
resetTimerBtn.addEventListener("click", () => {
chrome.storage.local.set({
// reset variables
timer: 0,
isRunning: false
}, () => {
// reset start button text-content
startTimerBtn.textContent = "Start Timer"
})
})In the preceding code, we did the following:
- Select the
Reset Timerbutton on the DOM via itsid. - Add a
clickevent listener to the button, with a callback function that resets thetimerandisRunningvariables in storage. - Finally, the
Start Timerbutton text is set to the string “Start Timer” based on the assumption it is currently “Pause Timer”.
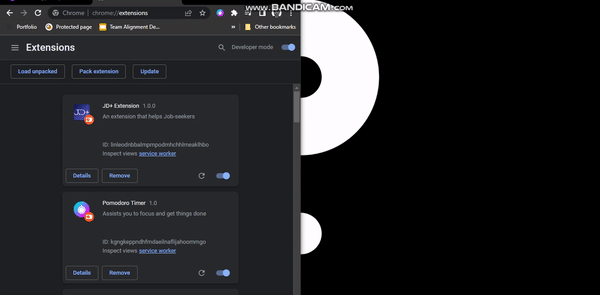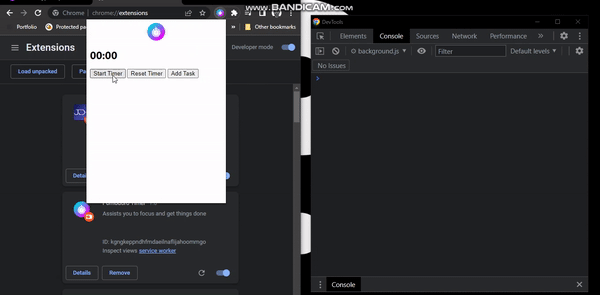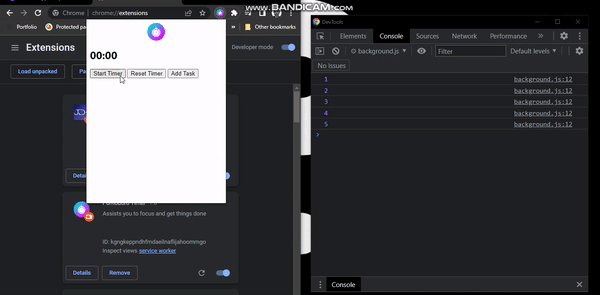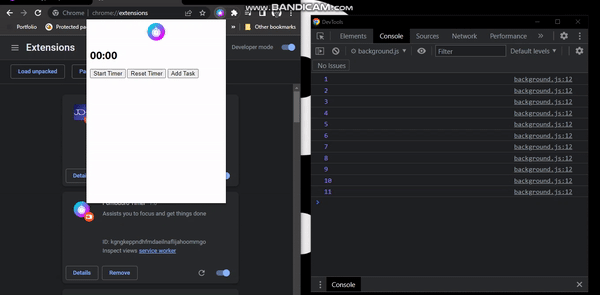
Displaying Time On The Popup
So far, we have been logging our timer values on the console. Let’s display it on the popup page.
In popup.html
<body>
<div class="header">
<img src="../icon.png">
</div>
+ <h1 id="time">00:00</h1>
<button id="start-timer-btn">Start Timer</button>
<button id="reset-timer-btn">Reset Timer</button>
<button id="add-task-btn">Add Task</button>
<div id="task-container">
<input type="text">
<input type="button" value="X">
</div>
</body>In popup.js
// array to store tasks
let tasks = [];
const time = document.getElementById("time");
// Update time every 1sec
function updateTime() {
chrome.storage.local.get(["timer"], (res) => {
const time = document.getElementById("time")
// get no. of minutes & secs
const minutes = `${25 - Math.ceil(res.timer / 60)}`.padStart(2, "0");
let seconds = "00";
if (res.timer % 60 != 0) {
seconds = `${60 -res.timer % 60}`.padStart(2, "0");
}
// show minutes & secs on UI
time.textContent = `${minutes}:${seconds}`
})
}
updateTime()
setInterval(updateTime, 1000)
// Start Timer ButtonIn the preceding code, we display the time on the popup page and update when any of the buttons that affect the timer are clicked. Let’s understand the code better:
- A bit of math is done in the
updateTime()function; the timer value is gotten from storage. - The minute for the timer is gotten(the timer should count down from 25mins) and stored in the
minutevariable. ‘25 - res.timer / 60— for example, if our timer value(res.timer) was120secs,120 / 60 = 2, then '25 - 2 = 23,i.e., 23 minutes will be left on the clock. - To get seconds we divide the timer value(
res.timer) by60. - The
minutesandsecondsvalues are displayed on the UI viatime.textContent. updateTime()is called automatically as the popup loads, and called every1secbysetInterval.
The time can now be seen on the popup.
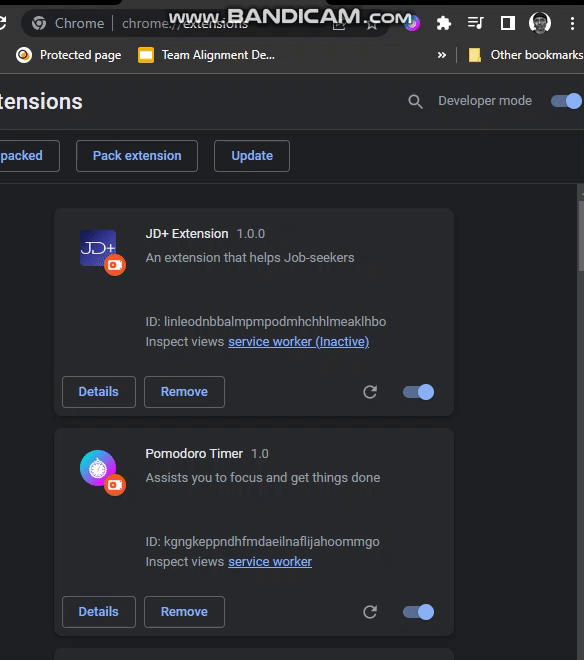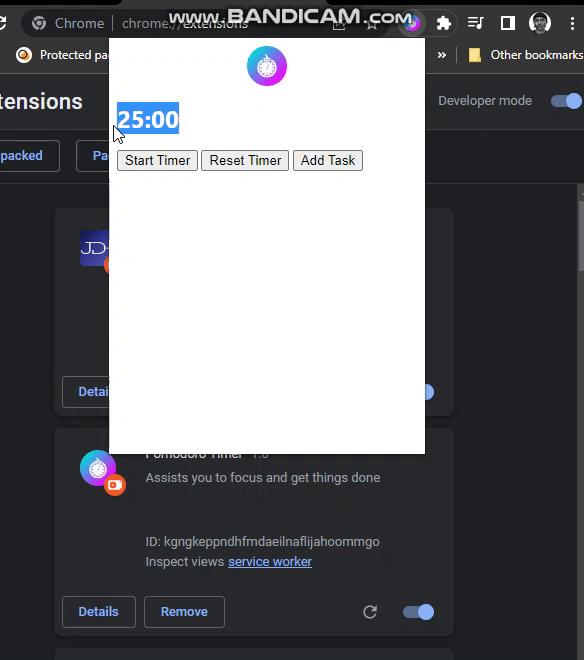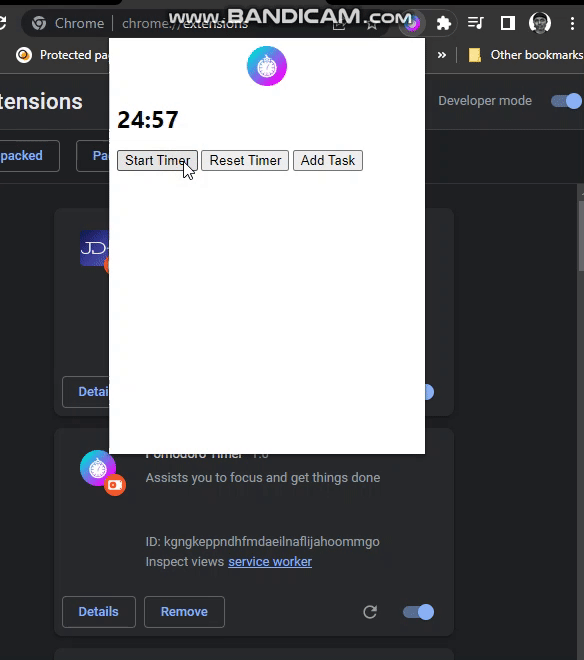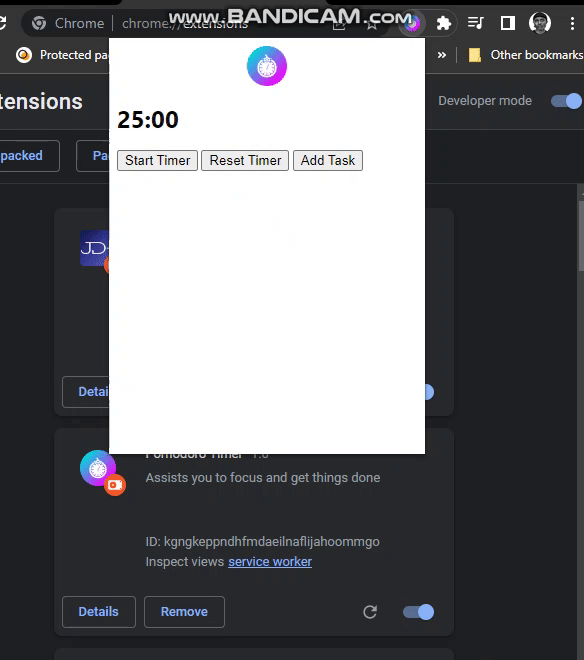
Sending Notification
Now, let’s set up notifications to notify the user when the time is up.
In background.js
// alarm listener
chrome.alarms.onAlarm.addListener((alarm) => {
if (alarm.name === "pomodoroTimer") {
chrome.storage.local.get(["timer", "isRunning"], (res) => {
if (res.isRunning) {
let timer = res.timer + 1
let isRunning = true
if(timer === 25) {
this.registration.showNotification('Pomodoro Timer', {
body: "25 minutes has passed",
icon: "icon.png"
})
timer = 0
isRunning = false
}
chrome.storage.local.set({
timer,
isRunning,
})
}
})
}
})In the preceding code, an if statement is used to check if our timer is up 25 minutes, then a notification is registered. When the timer expires, the timer value is reset to 0 and isRunning to false to pause the timer. To test this functionality, set the default value of the timer to 10secs(remember this is only for testing purposes, so we don’t wait for 25 minutes). In the if statement in the above code, change the timer value to 10secs— if(timer === 10). Now restart the timer, and after 10secs, you will see a notification.
Session Replay for Developers
Uncover frustrations, understand bugs and fix slowdowns like never before with OpenReplay — an open-source session replay tool for developers. Self-host it in minutes, and have complete control over your customer data. Check our GitHub repo and join the thousands of developers in our community.
Options page
We now have the basic functionality in place for the extension: we can start the timer, pause the timer, reset the timer, and delete and add tasks. Now, let’s make the extension more customizable so users can tailor it to their needs—Some users may want to focus on longer or shorter periods of time. We have to create an options page to enable the user to configure the extension. The user will be able to set the maximum time for a session to 1hour(60minutes) and the minimum to 1minute
Setting And Storing Option
Add the "options_page``` file in manifest.json.`
{
"manifest_version": 3,
"name": "Pomodoro Timer",
"version": "1.0",
"description": "Assists you to focus and get things done",
"icons": {
"16": "icon.png",
"48": "icon.png",
"128": "icon.png"
},
"action": {
"default_icon": "icon.png",
"default_title": "Pomodoro Timer",
"default_popup": "popup/popup.html"
},
"permissions": ["storage", "alarms", "notifications"],
"background": {
"service_worker": "background.js"
},
"options_page": "options/options.html"
}The options.html file is placed inside a folder to add structure to our project.
Create an options folder, and add the options.html and options.css files in it.
📦 Chrome-Extension-Series
┣ 🎨 icon.png
┣ 📄 manifest.json
┣ 📂 popup
┣ 📂 options
┃ ┣ 📄 options.css
┃ ┣ 📄 options.html<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
`<link rel="stylesheet" href="options.css">
<title>Pomodoro Timer Extension Options</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Pomodoro Timer Options</h1>
<input id="time-option" type="number" min="1" max="60" value="25">
<button id="save-btn">Save Options</button>
</body>
<script src="options.js"></script>
</html>In the HTML, we have a number input field with a minimum value of 1(1 minute) and a maximum value of 60(60 minutes). The value attribute contains our default timer value of 25(25 minutes). The Save options button will enable us to save options.
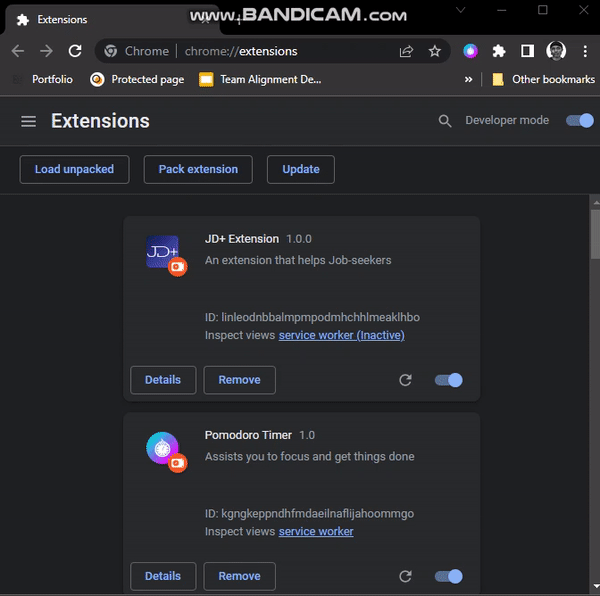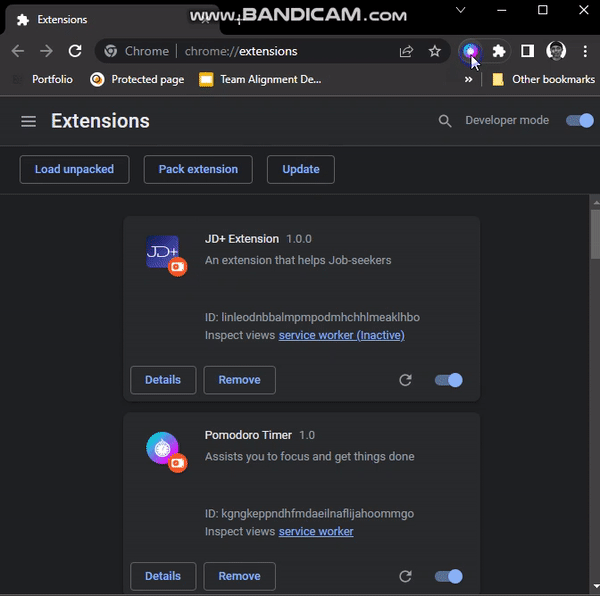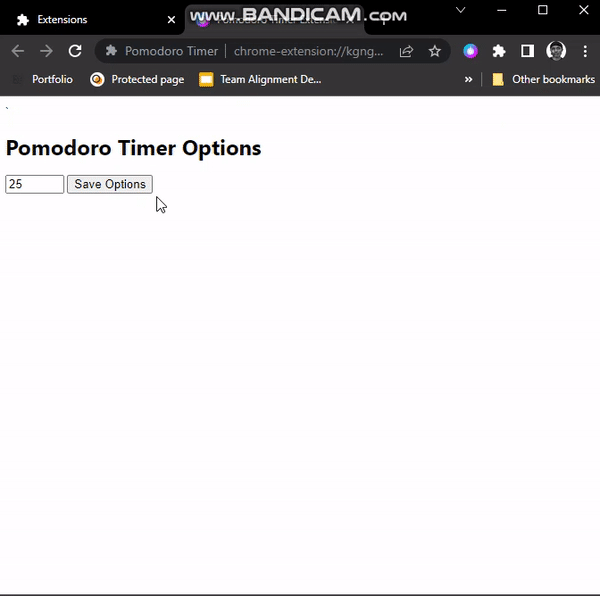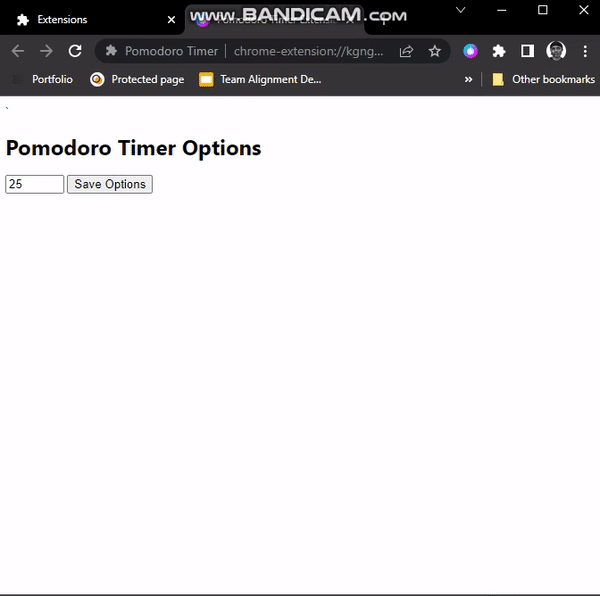
In options.js
// Add validation
const timeOption = document.getElementById('time-option')
timeOption.addEventListener('change', (event) => {
const val = event.target.value
if (val < 1 || val > 60) {
timeOption.value = 25
}
})
// Save Option
const saveBtn = document.getElementById('save-btn')
saveBtn.addEventListener('click', () => {
chrome.storage.local.set({
timeOption: timeOption.value,
timer: 0,
isRunning: false,
})
})
// Load Saved Option
chrome.storage.local.get(['timeOption'], (res) => {
timeOption.value = res.timeOption
})In the preceding code in option.js:
- We are validating the values passed in as options. It should not be less than
1or greater than60. - We store the new option, reset our timer, and set the
isRunningparameter tofalsewhen the timer setting is changed.
Displaying Saved Option On Popup
Now let’s read the saved through the background script and display it on the popup page.
In background.js
// create an alarm to notify user when time is up
chrome.alarms.create("pomodoroTimer", {
periodInMinutes: 1 / 60
})
// alarm listener
chrome.alarms.onAlarm.addListener((alarm) => {
if (alarm.name === "pomodoroTimer") {
chrome.storage.local.get(["timer", "isRunning", "timeOption"], (res) => {
if (res.isRunning) {
let timer = res.timer + 1
let isRunning = true
// console.log(timer)
if(timer === 60 * res.timeOption) {
this.registration.showNotification('Pomodoro Timer', {
- body: "25 minutes has passed",
+ body: `${res.timeOption} minutes has passed!`,
icon: "icon.png"
})
timer = 0
isRunning = false
}
chrome.storage.local.set({
timer,
isRunning,
})
}
})
}
})
// storage to set and track timer variables
chrome.storage.local.get(["timer", "isRunning", "timeOption"], (res) => {
chrome.storage.local.set({
timer: "timer" in res ? res.timer : 0,
timeOption: "timeOption" in res ? res.timeOption : 25,
isRunning: "isRunning" in res ? res.isRunning : false,
})
})In popup.js
// array to store tasks
let tasks = [];
const time = document.getElementById("time");
// Update time every 1sec
function updateTime() {
chrome.storage.local.get(["timer", "timeOption"], (res) => {
const time = document.getElementById("time")
// get no. of minutes & secs
const minutes = `${ res.timeOption - Math.ceil(res.timer / 60)}`.padStart(2, "0");
let seconds = "00";
if (res.timer % 60 != 0) {
seconds = `${60 -res.timer % 60}`.padStart(2, "0");
}
// show minutes & secs on UI
time.textContent = `${minutes}:${seconds}`
})
}If you test the extension by setting your option, you will see the new value on the popup page.
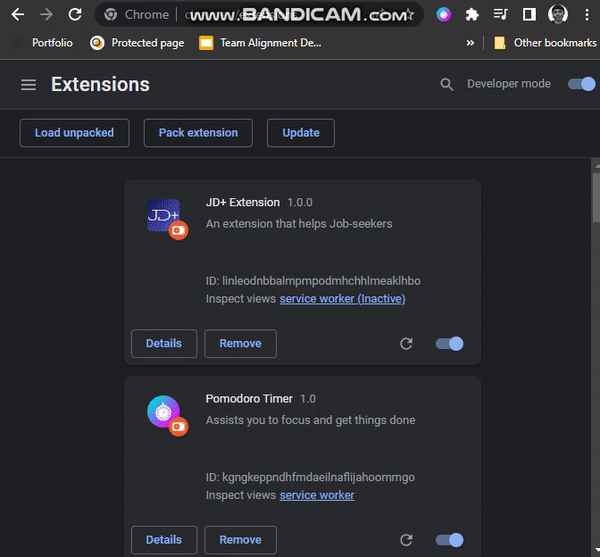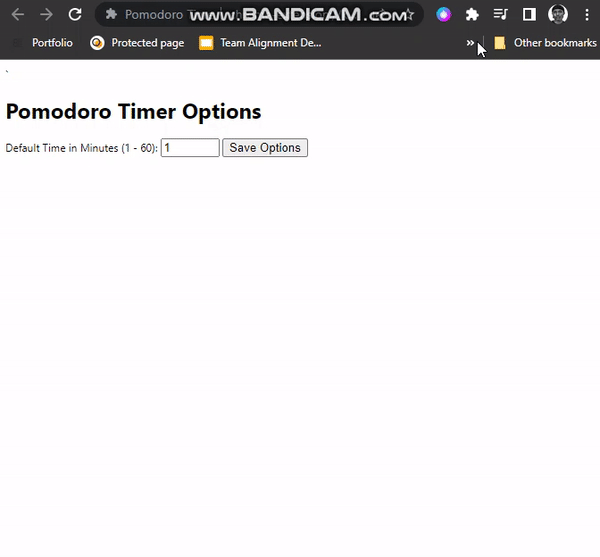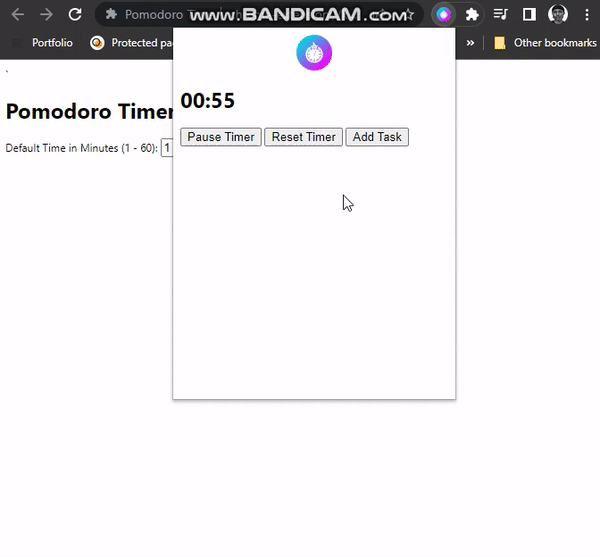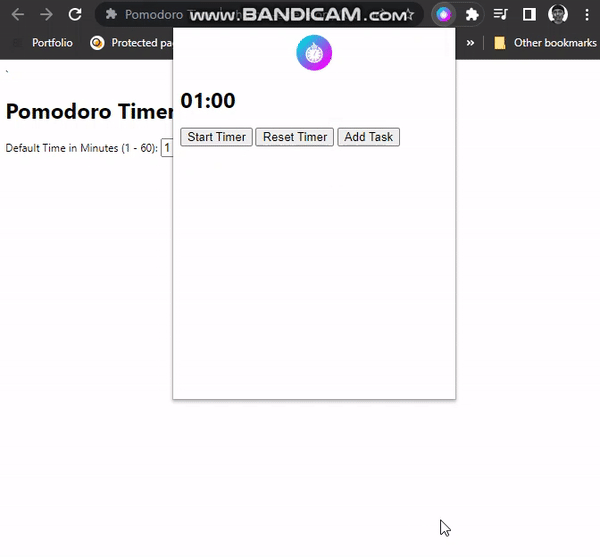
Styling
Finally, let’s style our extension. Copy and paste the code below.
In popup.css
body {
height: 400px;
width: 350px;
background: hsla(238, 100%, 71%, 1);
background: linear-gradient(
90deg,
hsla(238, 100%, 71%, 1) 0%,
hsla(295, 100%, 84%, 1) 100%
);
background: -moz-linear-gradient(
90deg,
hsla(238, 100%, 71%, 1) 0%,
hsla(295, 100%, 84%, 1) 100%
);
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(
90deg,
hsla(238, 100%, 71%, 1) 0%,
hsla(295, 100%, 84%, 1) 100%
);
filter: progid: DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient( startColorstr="#696EFF", endColorstr="#F8ACFF", GradientType=1 );
}
.header {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
height: 40px;
background-color: whitesmoke;
margin: -8px;
padding: 5px;
}
#time {
text-align: center;
font-size: 50px;
margin: 10px;
font-weight: normal;
color: whitesmoke;
}
#btn-container {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-evenly;
}
#btn-container > button {
color: black;
background-color: whitesmoke;
border: none;
outline: none;
border-radius: 5px;
padding: 8px;
font-weight: bold;
width: 100px;
cursor: pointer;
}
#task-container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
padding: 20px;
}
.task-input {
outline: none;
border: none;
border-radius: 4px;
margin: 5px;
padding: 5px 10px 5px 10px;
width: 250px;
}
.task-delete {
outline: none;
border: none;
height: 25px;
width: 25px;
border-radius: 4px;
color: indianred;
cursor: pointer;
font-weight: 700;
}In options.css
body {
background: hsla(238, 100%, 71%, 1) no-repeat;
background: linear-gradient(
90deg,
hsla(238, 100%, 71%, 1) 0%,
hsla(295, 100%, 84%, 1) 100%
) no-repeat;
background: -moz-linear-gradient(
90deg,
hsla(238, 100%, 71%, 1) 0%,
hsla(295, 100%, 84%, 1) 100%
) no-repeat;
background: -webkit-linear-gradient(
90deg,
hsla(238, 100%, 71%, 1) 0%,
hsla(295, 100%, 84%, 1) 100%
) no-repeat;
filter: progid: DXImageTransform.Microsoft.gradient( startColorstr="#696EFF", endColorstr="#F8ACFF", GradientType=1 );
}
h1 {
color: whitesmoke;
text-align: center;
font-size: 50px;
margin: 10px;
font-weight: normal;
}
h2 {
font-weight: normal;
color: whitesmoke;
}
#time-option {
outline: none;
border: none;
width: 300px;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 10px;
}
#save-btn {
display: block;
margin-top: 40px;
border: none;
outline: none;
border-radius: 4px;
padding: 10px;
color: black;
font-weight: bold;
cursor: pointer;
}
Conclusion
We have now come to the end of the Chrome Extension for Beginners series. I hope it has been helpful in getting you started with the basic concepts of building Chrome extensions. I encourage you to try building your own projects or even add more features to this project as a start. All the best with your learning.

