JavaScript's 'this' keyword explained and demystified

The this keyword is a double-edged sword—it can be a source of complicated errors and make life easier for you as a developer once you know how it works. These days, I feel that community pushes the language to more functional paradigms. We are not using the this keyword so much. And I bet it still confuses people because its meaning differs based on context.
So, in this article, the this keyword will be explained to give you a good understanding of how it works.
You will learn the following:
- What the
thiskeyword is in Javascript? - What the
thiskeyword represents in Node. - How the
thiskeyword is determined in the Global and Function Execution Context. - Different ways a function is invoked and how it relates to
this. - How to control the value of
thisusingcall()andapply()methods. - How to use the
bind()method. - How
thisbehaves in an arrow function.
What is the this keyword?
The this keyword is a variable used to store an object reference when a function is invoked in Javascript. The object the this keyword references or points to depends on the context this is used. Conceptually, this is akin to a pronoun in English because it is used to refer to an object—just as a pronoun refers to a noun.
For example: “Mary is running fast because she is trying to catch the bus.” In that statement, the pronoun “she” is used to refer to the antecedent (the noun that a pronoun refers to) “Mary”. Let’s relate this concept to the this keyword.
const person = {
name: "Mary",
pronoun: "she",
Activity: function () {
// this = person
console.log(`${person.name} is running fast because ${this.pronoun} is trying to catch the bus`)
}
}
person.Activity() // Mary is running fast because she is trying to catch the busIn the preceding code, this is used as a reference value of the person object, just like the pronoun “she” used to refer to “Mary”.
The this keyword is determined by the Execution context it is used in. In a nutshell, the Execution context is an abstract environment used by Javascript for code execution. It is of three variants:
- Global Execution Context
- Function Execution Context
There is also the eval() Execution Context, but it is rarely used due to its malicious nature. Read this article to learn more about the Execution Context.
this in the Global Execution Context
There are differences in the Global Execution Context if we work in a browser or Node; let’s see both cases.
In a Browser
In the Global Execution Context, the this keyword references the global object, the window object on the web browser.
console.log(window === this ) // true
this.color = 'Green'
console.log(window.color) // GreenIn the preceding code, a property is added to the global window object through the this keyword.
N/B: In the Global Execution Context, the this keyword will always reference the global object regardless of whether Javascript is in strict or non-strict mode.
In Node
As per NodeJS documentation
In browsers, the top-level scope is the global scope. That means that if you’re in the global scope var, something will define a global variable in browsers. In Node.js, this is different. The top-level scope is not the global scope; var something inside a Node.js module will be local to that module.
The above statement means that the this keyword does not reference the global object in NodeJS. Instead, it points to the current module it is being used in—i.e., the object exported via module.exports.
For example, let’s look at a hypothetical module called app.js
┣ 📄 app.js
console.log(this);
module.exports.color = 'Green';
console.log(this);output:
┣ $ node app.js
{}
{color: 'Green'}
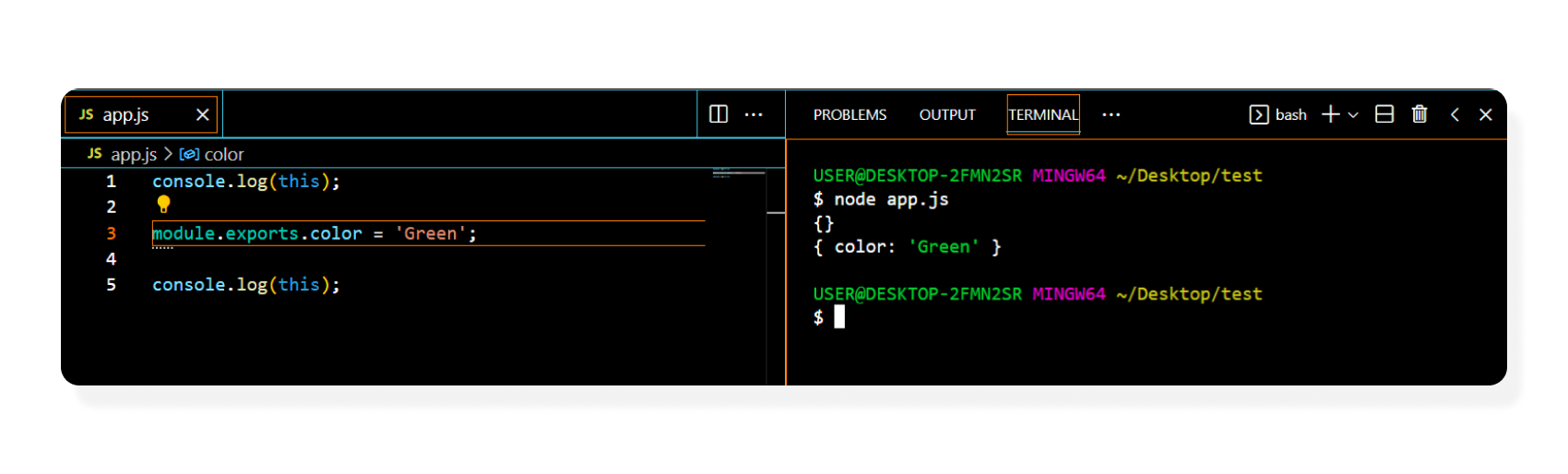
In the preceding code, an empty object is first logged because there are no values in module.exports in the app.js module. Then the color property is added to the module.exports object; when this is logged again, an updated module.exports object is returned with a color property.
Accessing the global object in Node
We now know that the this keyword doesn’t reference the global object in Node as it does in the browser. In Node, the global object is accessed using the global keyword, irrespective of where the global keyword is used.
┣ 📄 app.js
console.log(global);
output:
┣ $ node app.js
// logs the node global object
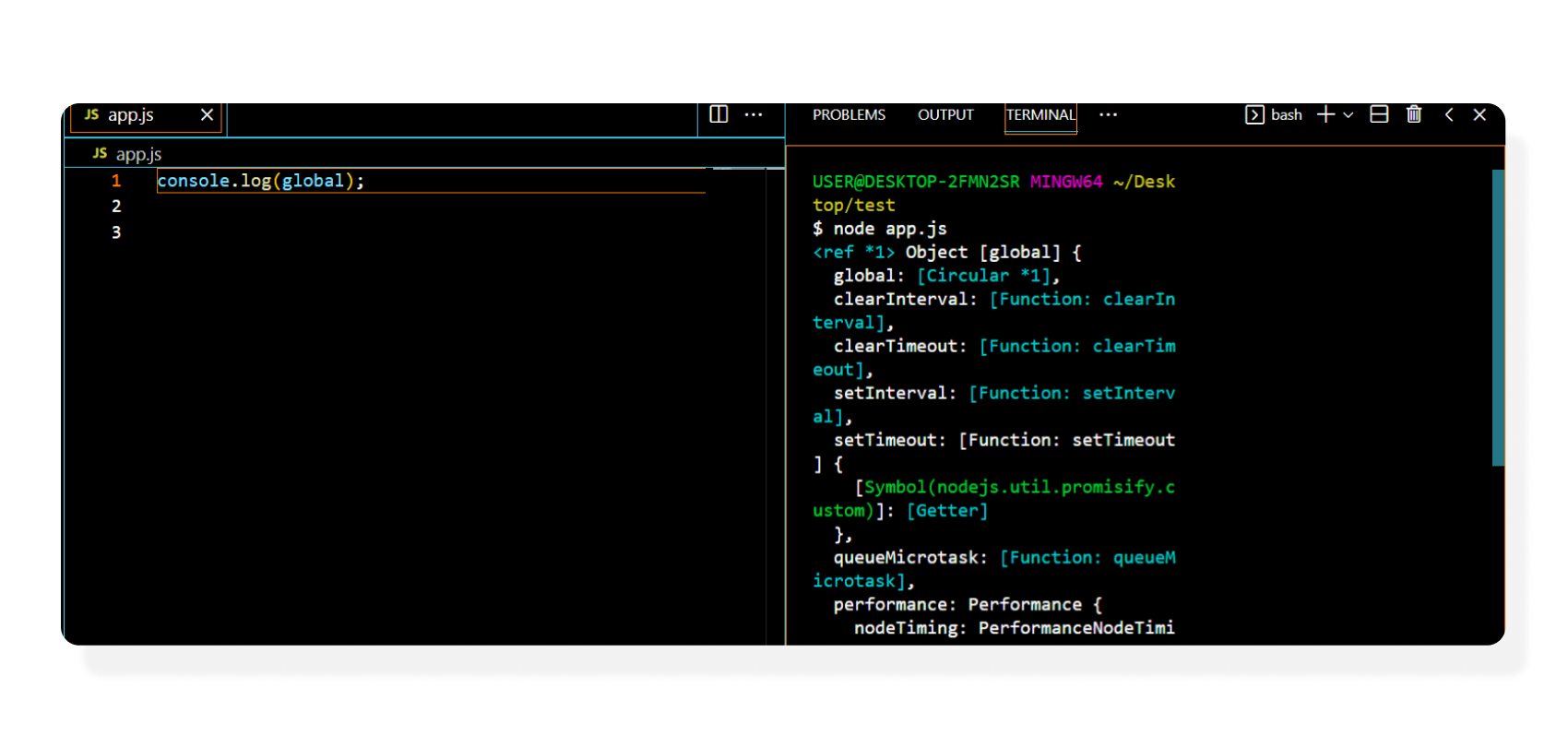
The global object exposes a variety of useful properties about the Node environment.
Open Source Session Replay
OpenReplay is an open-source, session replay suite that lets you see what users do on your web app, helping you troubleshoot issues faster. OpenReplay is self-hosted for full control over your data.
Start enjoying your debugging experience - start using OpenReplay for free.
Function Execution Context
In the Function Execution Context, how the this keyword is determined depends on how a function is called or invoked.
A Javascript function can be invoked in four ways:
- Invocation as a function
- Invocation as a method
- Invocation as a constructor
- Invocation with the apply and call methods
Invocation as a function
When a function is invoked as function(i.e when a function is called using the () operator), this references the global window object in non-strict mode and is set to undefined in strict mode.
Example
function A() {
console.log(this === window) // true
}
function B() {
"use strict"
console.log(this === window) // false
}
function C() {
"use strict"
console.log(this === undefined) // true
}
A(); // true
B(); // false
C(); // trueInvocation as a method
When a function is invoked as a method(i.e., via an object property), this references the method’s “owning” object.
Example
let Nigeria = {
continent: 'Africa',
getContinent: function () {
return this.continent;
}
}
console.log(Nigeria.getContinent()); // AfricaInvocation as a constructor
To invoke a function as a constructor, we precede the function invocation with the new operator.
Example
function Context() {return this; }
new Context();When a function is invoked as a constructor(via the new operator) a few actions take place:
- A new empty object is created
- This object is passed to the constructor as the
thisreference object—i.e., the objectthiswill point to when the function is invoked. - The newly constructed object is returned as the
newoperator’s value.
Example
function Person() {
this.name = 'Mary',
this.age = 20
}
const person1 = new Person();
console.log(person1.age) // 20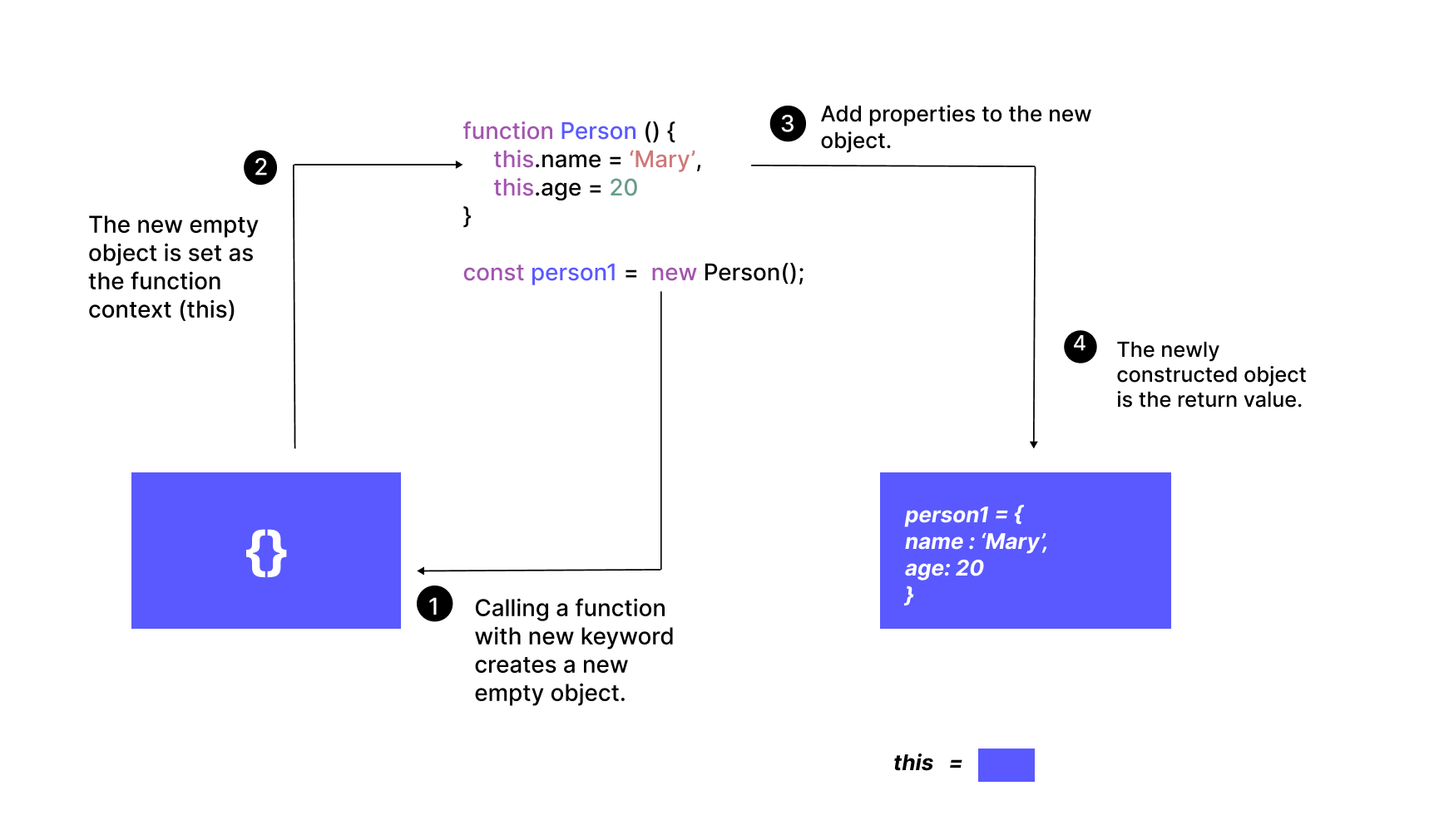
The preceding code and diagram show and explains how this will reference an object when a function is invoked as a constructor.
If you try to invoke a constructor function without the new operator, this will point to undefined, not an object.
Example
function Person() {
this.name = 'Mary',
this.age = 20
}
const person2 = Person();
console.log(person2.age)
// // => TypeError: Cannot read property 'age' of undefinedTo make sure that the Person() function is always invoked using constructor invocation, you add a check at the beginning of the Person() function:
function Person() {
if (!(this instanceof Person)) {
throw Error('Must use the new operator to call the function');
}
this.name = 'Mary',
this.age = 20
}
const person2 = Person();
console.log(person2.age)
// // => Must use the new operator to call the functionES6 introduced a meta-property named new.target that allows you to detect whether a function is invoked as a simple invocation or as a constructor.
You can modify the Person() function to use the new.target metaproperty:
function Person() {
if (!new.target) {
throw Error('Must use the new operator to call the function');
}
this.name = 'Mary',
this.age = 20
}
const person2 = Person();
console.log(person2.age)
// // => Must use the new operator to call the functionInvocation with call and apply methods (Indirect Invocation)
Functions are objects, and like all Javascript objects, they have methods. Two of these methods, call() and apply(), invoke the function indirectly. Both methods allow you to specify explicitly the this value(object reference) for the invocation, which means you can invoke any function as a method of any object, even if it is not a method of that object. call() and apply() also allow you to specify the arguments for the invocation. The call() method uses its argument list as arguments to the function, and the apply() method expects an array of values to be used as arguments. In both call() and apply(), the first argument is the this keyword—which represents the object on which the function is to be invoked.
Example
function getContinent(prefix) {
console.log(`${prefix} ${this.continent}`);
}
let nigeria = {
continent: 'Africa'
};
let china = {
continent: 'Asia'
};
getContinent.call(nigeria, "Nigeria is in");
getContinent.call(china, "China is in");Output:
Nigeria is in Africa
China is in AsiaIn this example, we called the getContinent() function indirectly using the call() method of the getContinent() function. We passed nigeria and china objects as the first argument of the call() method; therefore, we got the corresponding country’s continent in each call.
The apply() method is similar to the call() method, but as you already know—its second argument is an array of arguments.
getContinent.apply(nigeria, ["Nigeria is in"]);
getContinent.apply(china, ["China is in"]); Output:
Nigeria is in Africa
China is in AsiaArrow functions
In arrow functions, JavaScript sets the this lexically. This means the value of this inside an arrow function is defined by the closest containing “non-arrow” function. In addition, the value of this inside an arrow function can’t be changed, and it stays the same throughout the entire life cycle of the function.
Let’s look at some examples:
let getThis = () => this;
console.log(getThis() === window); // trueIn this example, the this value is set to the global object, i.e., the window object in the web browser. Let’s understand the preceding code more with the help of the stack and heap.
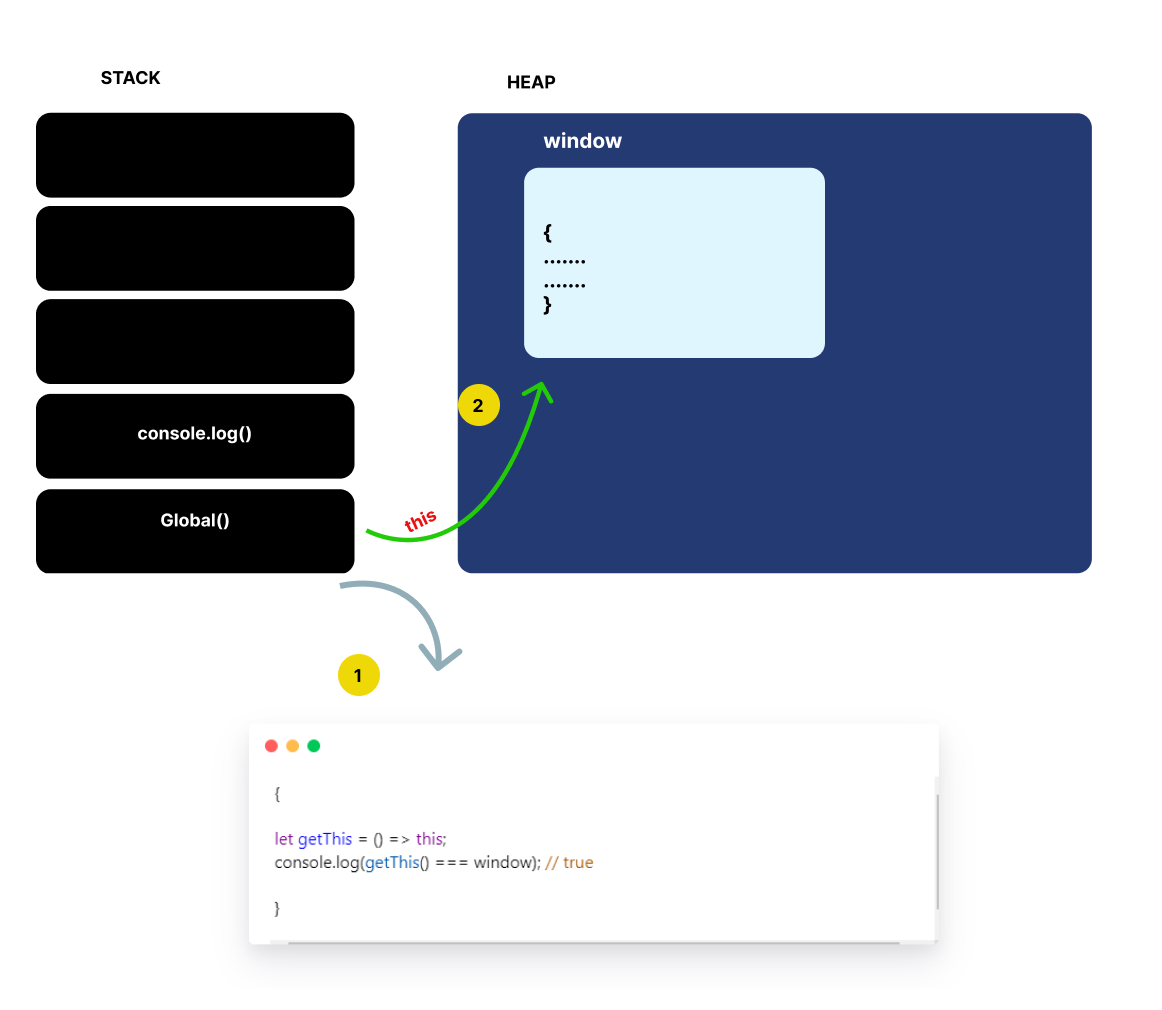
- The
getThisarrow function is lexically scoped to theGlobal()“non-arrow” function that returns globalwindowobject. - The
thisvalue in thegetThisarrow function is the globalwindowobject since thethisvalue is lexically scoped to point to this object.
Let’s look at another example:
function confirmThis () {
let getThis = () => this;
console.log(getThis() === window); // true
}
confirmThis();
Output:
trueSince the this value of a “normal” function points to the global window object in “non-strict mode”. The this value will also point to the window object since it is lexically scoped to the confirmThis() function. However, in “strict” mode, the case is different.
function confirmThis () {
"use strict"
let getThis = () => this;
console.log(getThis() === window); // true
}
confirmThis();Output:
falseThe this value of the confirmThis() function will be undefined in strict mode, same applies to the getThis arrow function.
Using the bind method
As per MDN
The
bind()method creates a new function that, when called, has itsthiskeyword set to the provided value, with a given sequence of arguments preceding any provided when the new function is called.
Example
const module = {
x: 42,
getX: function() {
return this.x;
}
};
const unboundGetX = module.getX;
console.log(unboundGetX()); // The function gets invoked at the global scope
// expected output: undefined
const boundGetX = unboundGetX.bind(module);
console.log(boundGetX());
// expected output: 42In the preceding code, the module object method getX() is invoked as a “function” (instead of a method of module) in the global scope. This causes it to lose its this reference to the module object. For this to still point the module object when the getX method is invoked as a “function” instead of a “method”, it needs to be “bound” to the module object via the bind() method—const boundGetX = unboundGetX.bind(module);.
Conclusion
Now you know how the this keyword works and the different contexts it applies. You should be able to use it comfortably when required.
Glossary
Stack or CallStack: A stack is a data structure that follows the Last in First Out(LIFO) principle. However, the execution stack is a stack that keeps track of all the execution context created during code execution. The stack also stores static data in Javascript(variables and reference values). Learn more here
Heap: The heap is a data structure storing dynamic data in Javascript. This is where all Javascript objects are stored. Learn more here.
Lexical scope: Read this stack overflow answer for better understanding.
Javascript strict mode: MDN
A TIP FROM THE EDITOR: For more on JavaScript’s internal details, don’t miss other articles by the same author: JavaScript Types and Values, explained, [JavaScript type conversions explained](https://blog.openreplay.com/javascript-type-conversions-explained, and Explaining JavaScript’s Execution Context and Stack.