Security and Privacy: Understanding GDPR

The General Data Protection Regulation, or GDPR in short, was implemented by the European Union. With this implementation, it’s mandatory for each and every business website to inform users of the data that they collect. Privacy issues sprung up due to breaches of several companies. Today, making a website GDPR-compliant is an absolute must to help protect users’ data, and this article will explain how.

Spot abnormal user behaviors and iron out the bugs early with OpenReplay. Dive into session replays and reinforce your front-end against vulnerabilities that hackers search for.
Discover how at OpenReplay.com.
Understanding GDPR
Across the globe, the GDPR is considered the most stringent and comprehensive security and privacy law. While it’s made and passed by the European Union, it imposes obligations to companies anywhere in the world that gather or target data from people in Europe. It was in May of the year 2018 that the regulation came into effect.
GDPR’s major purpose was to replace national laws that are no longer relevant to protect the personal information of the citizens of Europe. Under the GDPR, a person has the right to know the personal information being gathered, how the information is used, and where and with whom it’s shared. Europe has signaled its resolute stand on the privacy and security of information in these times wherein people are more and more entrusting their personal information with cloud services.
The Types of Data That Are GDPR Regulated
Today, any website collects different types of data, whether it uses any custom platform or is built from scratch. There are many ways for websites to gather information, which include analytics, contact forms, email marketing campaigns, subscription forms, and so on.
To put it simply, all personal data falls under the EU regulation. The following are some types of data that have been regulated by the GDPR.
- Biometric data
- Health and genetic information
- Gender, race, ethnicity
- Political/Religious views
- Web data, including cookie data and IP address
How Important Is GDPR Compliance to Your Website?
Since GDPR protects the privacy of users and ensures the protection of their information, it’s very important for a website to be GDPR-compliant. It applies to organizations big and small. Organizations should be ready for the change; otherwise, they could be at risk if they fail to comply.
The regulation serves as an opportunity for organizations to re-evaluate how they gather, store, share, and protect the data of the clientele. GDPR fosters trust and customer loyalty and enables an organization to position itself as a reliable and trusted source. Businesses could capitalize on new opportunities that arise from the GDPR with the right preparation.
Does Your Website Need to Be GDPR Compliant?
Is your website GDPR-compliant? If your website or solution is accessed by citizens of Europe, you must adhere to the GDPR. It’s advisable for all businesses and solutions to comply with privacy regulations; otherwise, they risk facing fines of up to 20 million pounds.
Furthermore, if you have a subscription function and a comments section, then you should comply with GDPR. Also, if users log into your website with third-party applications, then you are subject to complying with privacy regulations.
Steps to Make a GDPR-Compliant Website
The GDPR is indeed one of the most intimidating laws that businesses of all shapes and sizes have to deal with. Still, a lot of companies have no adequate grasp of the regulation, how it works, or how to become GDPR-compliant. How to make your website compliant with the GDPR depends on the measures you have undertaken and which you don’t.
Understand How You Gather Data
Knowing and understanding how you gather data, how you store it, and who can access it is the key. Check out the following checklist.
- Does the data you gather collect personal data from minors?
- Does the data include sensitive information? What are your safety measures for sensitive data?
- What personal data are you holding?
- Why do you require personal data?
- In what way did you get consent to process personal information?
- Who gets data access?
- Where do you store this data?
- Are there third parties holding the personal data? If yes, how is it controlled?
- How long is personal information stored? Can any information be anonymized or deleted?
Display Cookie Notice
A cookie Notice or Banner is a necessity if your website collects data from Europe-based users to get consent for storing cookies on their different devices. The notice serves to inform users that the website is using cookies and the data that they collect. Furthermore, it should inform users of their right to refuse the use of cookies and the collection of personal data. Also, if information has been collected already, the notice should inform the user of his/her right to request the deletion of personal information.
Keep in mind these basic things:
- The notice should have an opt-in or an opt-out option for users to accept or reject cookies.
- Describe the kind of cookies you will set and why.
- Explain why you set cookies.
- Avoid dropping cookies prior to the user’s explicit consent.
- Not interacting with the banner or scrolling over the page does not mean Cookie Consent.
- Include information regarding your Privacy Policy and its link.
- Provide a possibility to enable Cookie consent based on the cookie category.
- Make the website accessible even if the user does not allow cookies.
- Provide a possibility to change or withdraw Cookie Consent status on every website page.
- All user consent should be documented and stored.
Take a look at how Openreplay is displaying cookie notices on their website. You can also see that they’ve also added a link going to their privacy policy page for more information about what they’re collecting.

Here are some more examples of clear Cookie Notices.
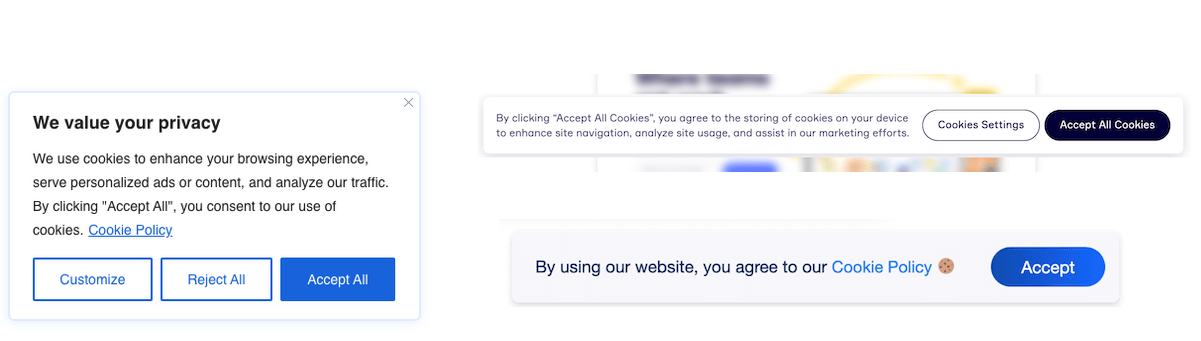
Make Website Security a Top Priority
As a webmaster, your topmost priority should be security. This not only helps keep data stored secure, but it also means the security of the website from malicious intent. Websites are the usual target of hackers and attackers.
How do you ensure website security? Check out the following:
- Ensure the security of data between the host and the webpage by setting up an SSL certificate.
- For banking details, the server should have additional security levels.
- Careful password protection of administrative accounts.
- Protect the website from malicious users by using an anti-virus or similar service.
- Refrain from giving out private information to random websites, particularly if it’s sensitive data.
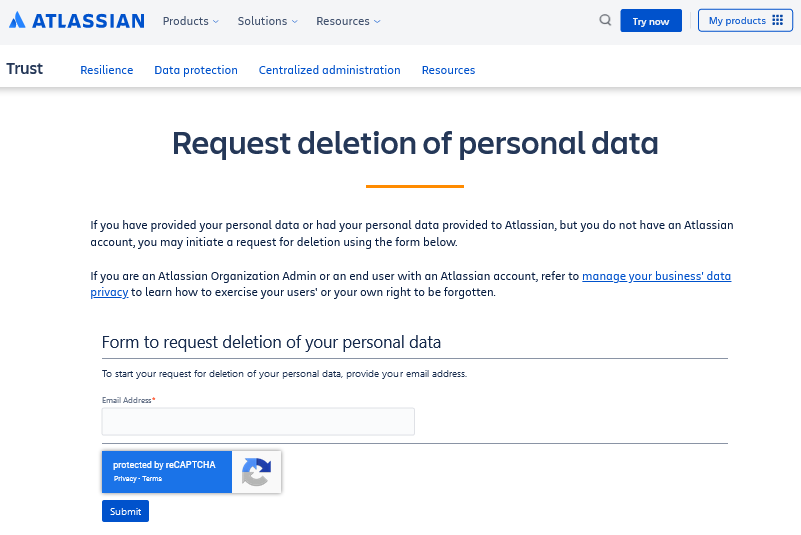
Delete Personal Data Upon Request
GDPR provides users the right to be forgotten, meaning that they can request the deletion of their data. An organization should always do as per user request. Deleting or removing data includes removing users from your mailing lists, wiping any personal information you have on them, and deleting their accounts.
Keep in mind that even forum comments and blog posts count as personal data, and you should remove them upon request.
Under the GDPR, processors and controllers of data have an obligation to delete or return all personal information after the end of the services or during the expiration of the contract or agreement unless otherwise stipulated by law. The right to erasure means an individual could demand the data to be deleted if it’s no longer relevant for the purpose it was collected.
Comprehensive Privacy Policy Implementation
A thorough privacy policy that outlines how information is gathered and how it will be used and shared should be included. The following are what you should include in your comprehensive privacy policy.
- Never disclose private information unless required by law.
- It’s good if you did not profit from selling access to your user’s personal data. It’s a great help if you do not profit from selling access to the personal information of users.
- How you use the data collected and the information gathered.
- The categories of the data that you collect.
- The measures undertaken to ensure data and information privacy.
- The privacy policy should be as understandable and straightforward as possible by using direct wording that leaves no room for ambiguity.
Moreover, you can follow complete guidelines on Writing a GDPR-compliant privacy notice and also be able to download a free template.
Evaluating Contact Forms
If you have different types of forms, such as in particular, contact forms that collect data, make sure to:
- Add an opt-in option to get the consent of the user to gather data, such as a disabled toggle switch or an unticked checkbox.
- You must have a privacy statement that explains the reason why you’re asking for details and what you will do with these details, and inform users that they could withdraw their consent anytime.
- It’s preferable to add a Privacy Policy link for further information.
- Add a checkbox so people can opt to receive correspondence from your website or other related services.
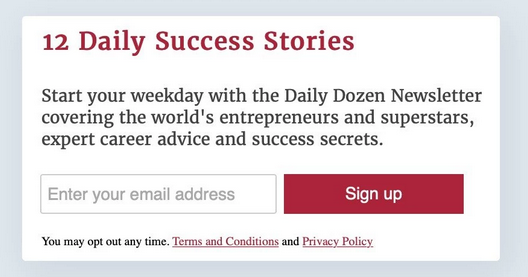
Some examples of GDPR-compliant Forms from big businesses.
An example from Forbes with a privacy policy link in the opt-in form.
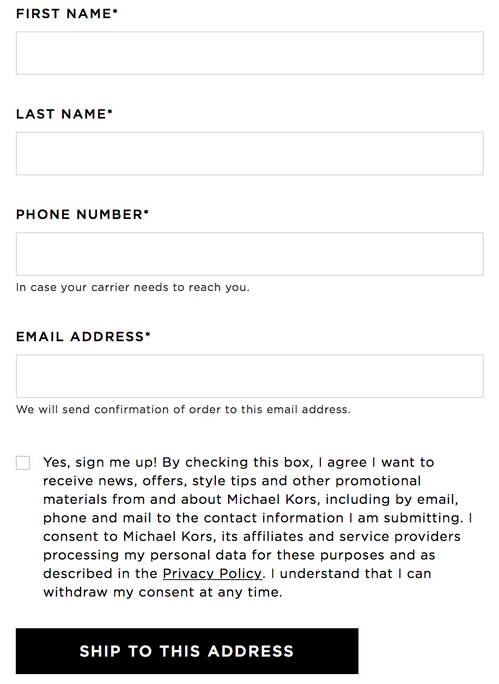
An example from Michael Kors of checkbox example.
Email Consent Management
If you make use of email marketing to send newsletters or emails to any other EU users, you should ask permission from users. Users from Europe should give permission to send these emails. Furthermore, EU users should give opt-in consent to receive emails from you.
Moreover, users should also be able to opt out of emails should they wish to do so. Provide an unsubscribe link in the email that could be easily found by your users. After a user clicks on the unsubscribe link, it should lead the user to a page where he can unsubscribe from emails easily without having to justify his choice.
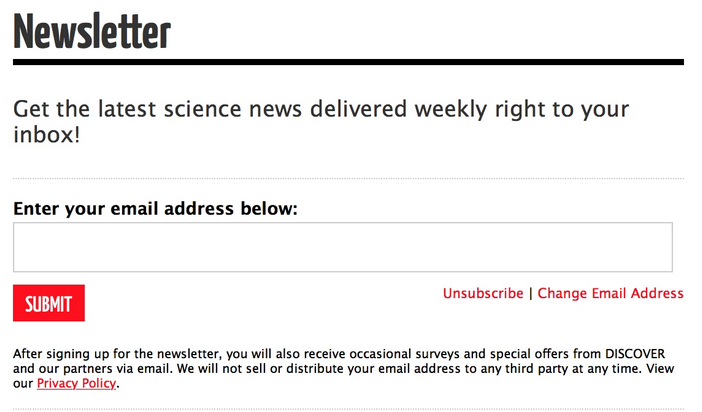
Here’s an example from Discovery magazine with a clear mention of an unsubscribe link.
Appoint a Data Protection Officer if Needed
Individuals and small companies may not need an in-house data controller. However, if your website gathers a lot of data or operates in several countries, then having a Data Protection Officer is necessary. The task of the DPO is to make sure that the organization adheres to all the requirements of the GDPR.
These include customer data protection and quick response to any request or complaint. Furthermore, they could provide legal advice in case of a discrepancy in website compliance.
Check Third-Party Services
You should check out which third-party services that your organization directly uses. You should, furthermore, be aware of the privacy policies of a third-party service or company that you directly or indirectly use.
If they’re performing work on your behalf, then you should make sure that they align with your company’s privacy policy. Meaning that they should also be compliant with the regulation. Here’s a great resource about How to work with third-party services under GDPR. You can find some questions you should ask from your service provider before signing any contract or subscribing.
For instance, many organization’s websites integrate email marketing tools in order to serve their customers with offers. Those marketing tools will act as a third party, and the data you’re sharing with them comes under GDPR. So, make sure the tools you’re using should have a proper privacy policy page mentioning everything about how they’re processing the accumulated data.
Conclusion
The bottom line is that being GDRP compliant is worth it. Despite the fact that the penalties under the regulation are big enough for you to worry, it’s important to keep in mind where the regulation came from. The major goal is to safeguard ordinary people from many online cybercriminals.
In today’s privacy-conscious world, the ability to ensure transparency and security of your app is a huge advantage. The GDPR is a major factor in the trend toward more international web regulation. The regulation should not be taken lightly.
Business organizations, big or small, that process the personal data of EU users should implement the regulations right away to ensure a secure environment. A safe environment, after all, always encourages a scope for ample opportunities. The GPDR is not about fines; it’s about accountability and transparency while protecting personal information. Moreover, GDPR is good for your business, and being in business makes it all the more reason to comply with it.
Secure Your Front-End: Detect, Fix, and Fortify
Spot abnormal user behaviors and iron out the bugs early with OpenReplay. Dive into session replays and reinforce your front-end against vulnerabilities that hackers search for.

