Why is Website Performance Important?

Website performance analyzes your website’s responsiveness and how quickly it loads, providing information that can optimize your site and make it as user-friendly as possible. Your website’s loading speed, not its content, is the most crucial aspect in determining its worth. Simply put, the performance of your website is crucial to its long-term success.
Website performance has a significant influence on your business since it determines how accessible and usable your website is. The main reasons for maintaining your website’s performance are mentioned below.

Conversion Rate
When a user completes a desired action on your website, such as completing a transaction, downloading an ebook, or filling out a contact form, this is known as a website conversion. Each business website is designed to increase conversions. The actions used to measure the conversion rate depend on the business goals of a website.

A website’s conversion rate typically ranges from 2 to 5 percent. Higher than 5% website conversion rates are regarded as “good” or above average. Furthermore, leading brands in several industries get far superior outcomes to 10%.
Conversion Rate can be measured using Google Analytics 4.
Bounce Rate
The bounce rate is the proportion of visitors that abandon a website after just seeing one webpage. Users will probably click away or close the window if a website doesn’t load in a few seconds.
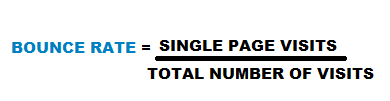
If 100 users visited your site and 10 of them left after visiting a single page, then your bounce rate is 10/100 = 10%
According to the Kibo Q2-2022 report, the bounce rates in e-commerce range from 20% to 45% on average.
Google Analytics 4 can be used to calculate bounce rates.
SEO best practices
Site performance is a significant element in Google search rankings since Google favors providing people with relevant information as soon as workable. The following SEO practices can be followed to optimize your site’s performance:
Generate content based on target keywords
Search intent, sometimes referred to as “user intent,” is what drives every search query. Understanding and executing users’ search intents is Google’s primary goal. The websites included on page one all meet Google’s requirements for search intent. For example, look at the search results for ‘bake chocolate chip cookies’:
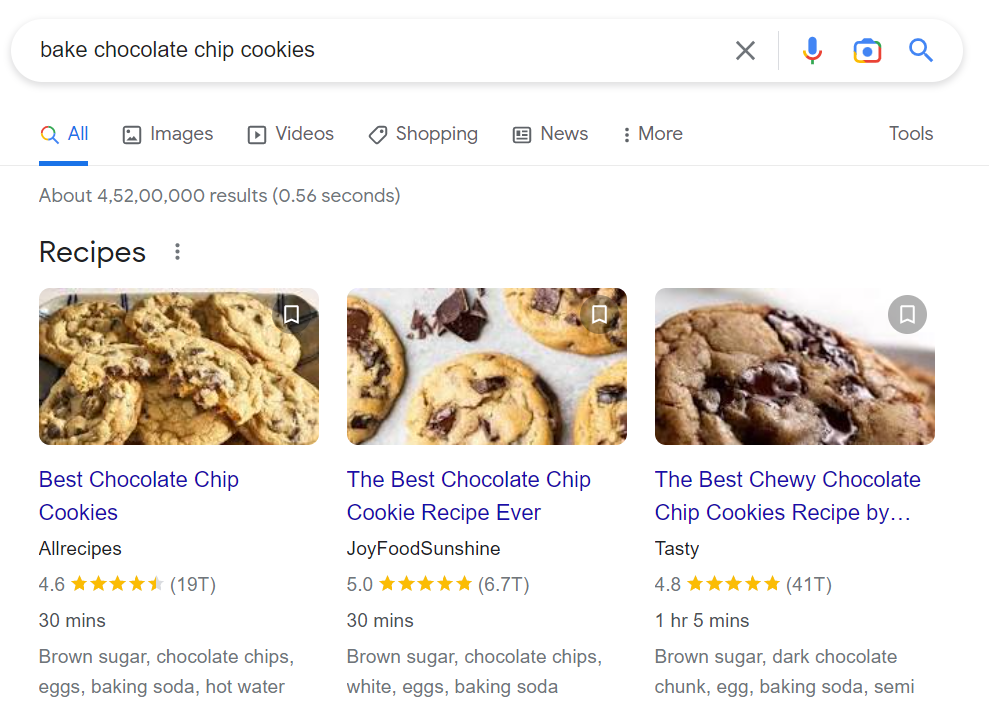
All the top search results are those of blogs and not product ads, as the user’s intent is to look up recipes. Let us now look at the search results for ‘shop chocolate chip cookies’:
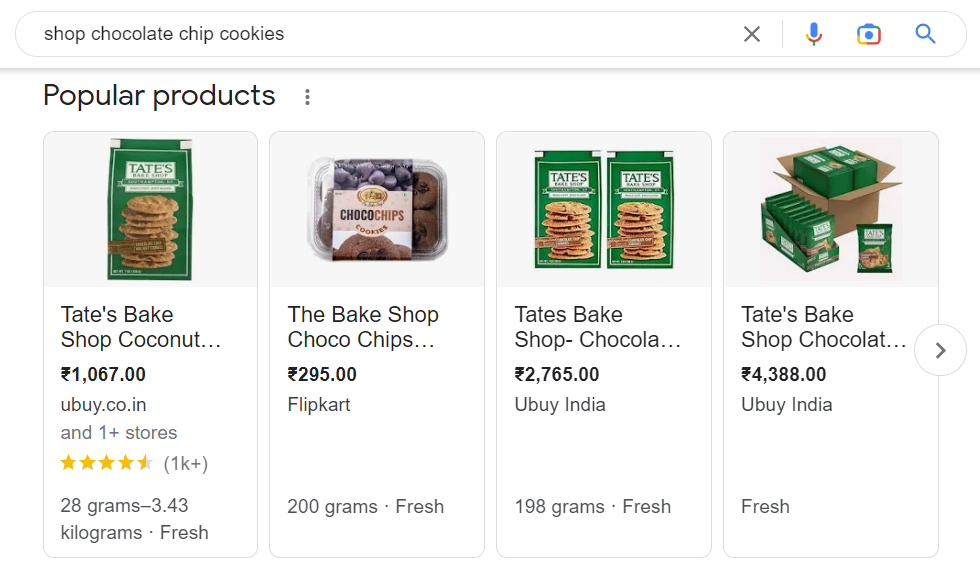
The above displays links to all pages where users can buy chocolate chip cookies. Google understands the user’s intent to buy in this case. Understanding users’ intent and producing related content are prerequisites for ranking amongst Google’s top search results.
Use of catchy Title Tags
In SERPs(search engine results pages), title tags are clickable headlines. They inform Google what the subject of your page is. And they are essential in terms of SEO. A title tag appears like this in Google’s search results:
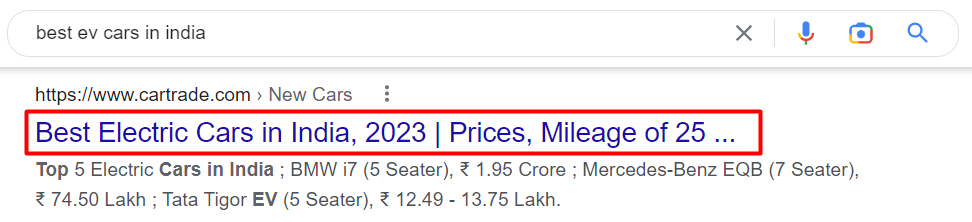
Title tags are essential for consumers to quickly understand the content of a result. Searchers often use it as their primary source of information when choosing which result to click on. Hence, it’s crucial to have intriguing names on your website. Title tags should be around 50 to 60 characters long.
The following is the HTML code for the above Title Tag:
<title>Best Electric Cars in India, 2023 | Prices, Mileage of 25 Electric Cars</title>Optimize Images
A page’s total size and loading time are frequently heavily influenced by its images. JPEG and PNG are the two picture file types most often used online. The file sizes between these two might vary significantly as they use different compression techniques. Hence, choosing the correct file format is a crucial step.
Example:

Add a lot of internal links
Internal links are crucial because they provide a hierarchy of information on your page. They also assist Google in comprehending the information on your website. Internal links can improve your results when appropriately implemented.
Create solid meta descriptions
A page’s content can be summarised using a meta description tag. It frequently appears on the SERP(search engine results pages) below the page’s title and URL. The meta description should give viewers a precise overview of the page’s content.
Example :
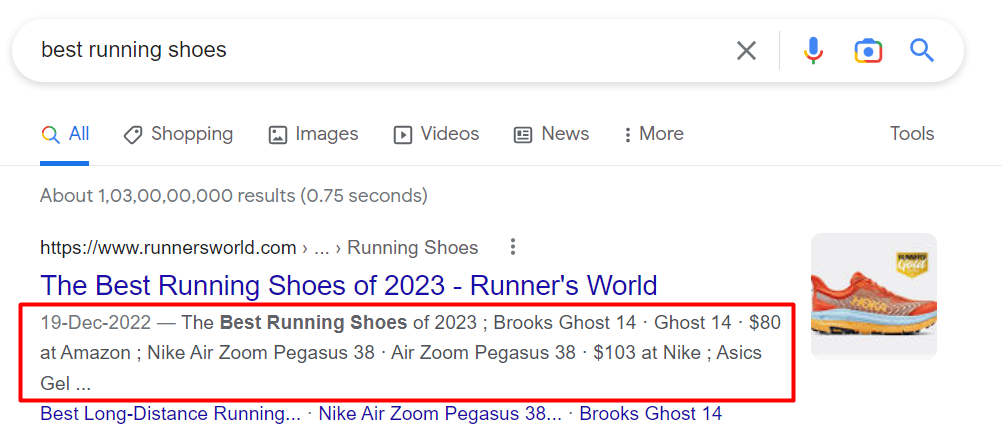
They operate as a sales pitch, persuading searchers that the page is just what they seek. Google often cuts off meta descriptions at 155–160 characters.
The following is the HTML code for the above meta description:
<meta name="title" content="The best running shoes 2023">
<meta name= "description" content=" Looking for the best running shoes in 2023? We list the best men's running shoes and the best female running shoes, tested on the road and in our Runner's World test lab.">
<meta name= "keywords" content= "running, running shoes, best running shoes, 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022, 2023, sneakers, trainers, sneakerhead, Nike, adidas, brooks, asics, puma, reebok, saucony, under armour, ultraboost, flyknit, vaporfly, everun, HOVR, freeride,">
<meta content= "These are the running shoes that came out on top in our spring and autumn 2023 shoe tests" property="og:title">
Make the layout user-friendly on both desktop as well as mobile
You don’t have to replicate your website layout for desktop and mobile devices. Cloaking might result from this, which is against Google Webmaster Guidelines.
Use a responsive design that enables you to use the same information on both desktop and mobile, as an alternative. In responsive design, media queries seamlessly transition your website’s design across platforms and devices.
Use the sitemaps and navigation
A sitemap ensures that search engines can find and crawl the most important pages on a website. Sitemaps also make it easier to navigate your website by assisting with comprehending its layout. Sitemaps also aid in understanding the layout of your website, making it simpler to explore.
User Experience
One of the biggest issues for website owners is specifically reaching potential users and retaining them for longer. The possibility of a user’s retention also increases when they are thoroughly satisfied with their website encounter. Therefore, user satisfaction is an important metric to assess a website’s performance. Various tools can be used to measure customer satisfaction. One of them is Delighted.
- Promoters: Customers who rated 9 to 10 on their satisfaction surveys
- Passives: Customers who rated 7 to 8 on their satisfaction surveys
- Detractors: Customers who rated 0 to 6 on their satisfaction surveys
The following qualitative metrics can be evaluated using Delighted:
-
NPS (Net Promoter Score): NPS is a customer success indicator that gauges client loyalty and satisfaction. NPS score is calculated by adding all your replies and dividing the ratio of promoters by the number of detractors. Your NPS would be 60-10=50; for instance, if 60% of respondents are promoters, 10% are detractors, and 30% are passives.
-
CSAT (Customer Satisfaction): CSAT score gauges a customer’s enjoyment of a product, service, or customer support encounter via a survey. Your score is calculated after your clients grade you on a scale of 1 to 5.

-
CES (Customer Effort Score): CES is a statistic for measuring the level of user effort required to execute a purchase, handle a support case, or connect with your business or product in general, whether online or in person. Your score is calculated after your clients complete a CES survey and grade your efforts on a scale of 1 to 5 or 1 to 7, depending on what grading scale you choose for your company.
Depending on preference, the following methods may be used to conduct the surveys:
-
Text message
- Sent: Total number of SMS surveys sent
- Responded: Total number of SMS surveys that received a response
- Commented: Total number of SMS responses that included a comment
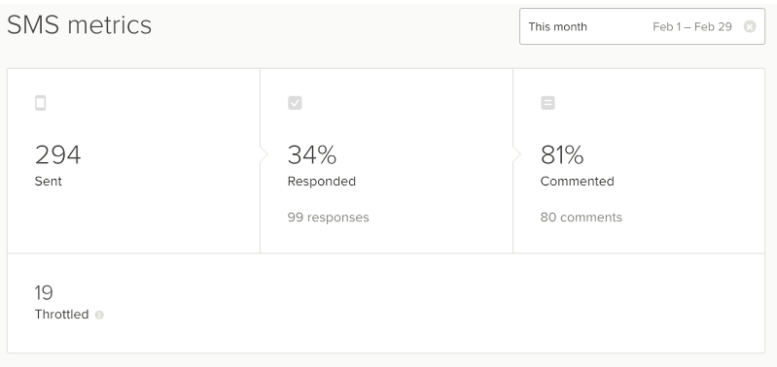 Source: https://help.delighted.com/article/548-the-metrics-tab
Source: https://help.delighted.com/article/548-the-metrics-tab
-
Email
- Sent: Total number of emails sent for surveys
- Opened: Total survey emails that were opened (even if no response was submitted)
- Responded: Total number of survey emails that received a response
- Commented: Total number of comments made: Commented responses received
- Bounced: The total number of survey emails that failed to deliver after being sent
- Unsubscribed: The total number of survey emails that led to the cancellation of Delighted survey subscriptions.
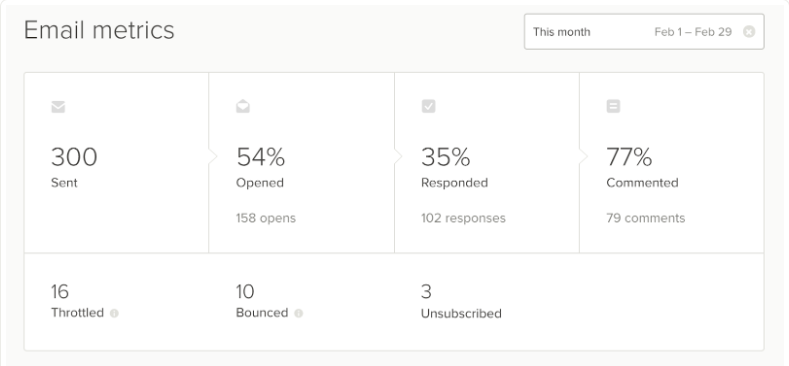 Source: https://help.delighted.com/article/548-the-metrics-tab
Source: https://help.delighted.com/article/548-the-metrics-tab
-
Website
- Shown: Total number of times the online survey was shown is displayed
- Responded: Total number of responses web survey received
- Commented: The total number of comments in the responses
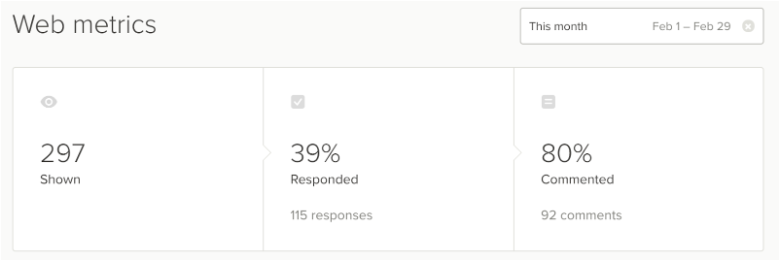 Source: https://help.delighted.com/article/548-the-metrics-tab
Source: https://help.delighted.com/article/548-the-metrics-tab
After the data is gathered, it is presented in a simple, user-friendly, and engaging layout as below.
 Source: https://help.delighted.com/article/548-the-metrics-tab
Source: https://help.delighted.com/article/548-the-metrics-tab
Session Replay for Developers
Uncover frustrations, understand bugs and fix slowdowns like never before with OpenReplay — an open-source session replay tool for developers. Self-host it in minutes, and have complete control over your customer data. Check our GitHub repo and join the thousands of developers in our community.
Factors that affect website performance
A successful website is made up of many components, and the majority of them affect overall performance. The major factors that might impact website performance are listed below, along with suggestions for improving them.
Page weight
The amount of resources a website needs to load considerably impacts how quickly it loads. Multimedia content, large CSS/JavaScript files, high-resolution photos, etc., significantly increase a webpage’s loading time. There are several techniques to reduce the file size of your website:
Design a website more simply. Reduce the number of files visitors download while browsing your website using a simple and straightforward theme.
Make code files smaller. Remove all white spaces, line breaks, and comments from the code files of your website.
Reduce the number of ads that take up additional resources. Don’t overdo it; display them where it makes sense.
Internet Connection
Your website’s load time is strongly impacted by the type of internet connection you use. No matter how effectively you optimize your site, it will take longer to load if you still use a 3G network or other dial-up connections.
Consider a variety of internet connections when selecting the best one for your website. The first option is DSL, which offers a quicker connection than dial-up. You may start using DSL and cable connections, which will meet all your website demands and produce faster loading times.
Hosting location
The physical location of your server plays a crucial role in how quickly your website loads. Data transfer will be slowed if your servers are far away, and your users will experience site delays. Data will be sent more quickly between servers near your target audience.
The solution is using a CDN(Content Delivery Network). A CDN is a network of servers located all over the world. The CDN stores a cached copy of your website’s content in multiple locations. It reduces the latency by minimizing the distance between the user and the server. When users click on your website, their browser loads some content from the closest CDN server. The remaining content is loaded onto the hosting server. A CDN lessens server strain and enhances response times if your customer base is global.
Website Performance Metrics
Your website’s performance metrics will give you information about how it is doing and whether any changes need to be made to make it more user-friendly for future users.
Load Time
The time it takes for a webpage to load in a browser indicates how quickly each HTTP request will be processed. Since a variety of resources must be loaded in addition to the page’s core HTML, almost every webpage on the Internet must make many HTTP requests.
Use Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool to evaluate load time.
Page size
Page size is the file size of all the resources that need to be loaded for it to function properly. The size of the page is directly proportional to how quickly the browser loads a webpage. We can check page size using Google’s PageSpeed Insights tool.
Time To First Byte (TTFB)
This metric assesses how long a browser takes to request a webpage before receiving the first byte of the answer.
The following tools can be used to test TTFB:
Round Trip Time(RTT)
The term “round trip time” (RTT) refers to the time needed for a data packet to travel from a particular source, such as the computer sending the signal, to a distant computer or system and back.
RTT is commonly calculated using the Ping, a command-line tool, and expressed in milliseconds. The Ping command is a command-line utility that calculates how long a data packet takes to go from one location to another and back again.
Tools to measure Website’s Performance
The following tools measure the website’s performance. They show you how fast or slow your website loads. They also indicate areas that can be improved to optimize your website’s performance.
Google’s PageSpeed Insights (PSI)
Google’s Page Speed Insights(PSI) provides page speed scores for both the desktop and mobile versions of the website and examines the content of a webpage. It displays a final grade summarising the simulated performance of the page. Any score between 50 and 90 requires improvement; a score below 50 is considered bad, and a score of 90 or more is considered good.
Following is the report summary for global retail giant H&M’s desktop version :
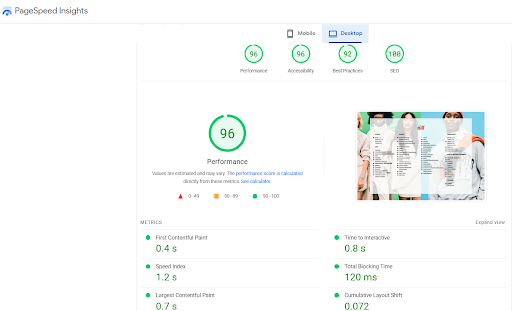 Source: https://pagespeed.web.dev/report?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww2.hm.com%2F&formfactor=desktop
Source: https://pagespeed.web.dev/report?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww2.hm.com%2F&formfactor=desktop
Firefox Network Monitor
Most browsers have features you can use to assess the performance of loaded sites. Consider the example of Firefox Network Monitor. It provides comprehensive details on all the resources downloaded from the network, along with a time graph displaying how each resource was downloaded.
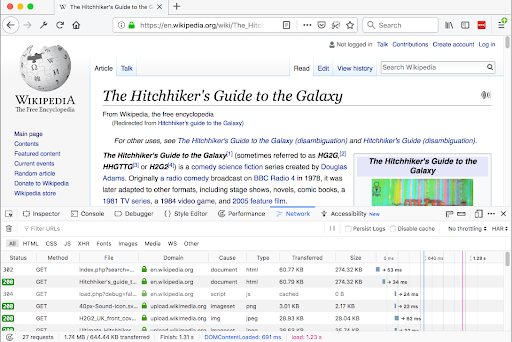 Source: https://firefox-source-docs.mozilla.org/devtools-user/networkmonitor/
Source: https://firefox-source-docs.mozilla.org/devtools-user/networkmonitor/
Google’s Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of specific factors that Google uses to analyze a webpage’s overall user experience. They are made up of the largest contentful paint (LCP), first input delay (FID), and cumulative layout shift (CLS). Core Web Vitals will be part of Google’s page experience score.
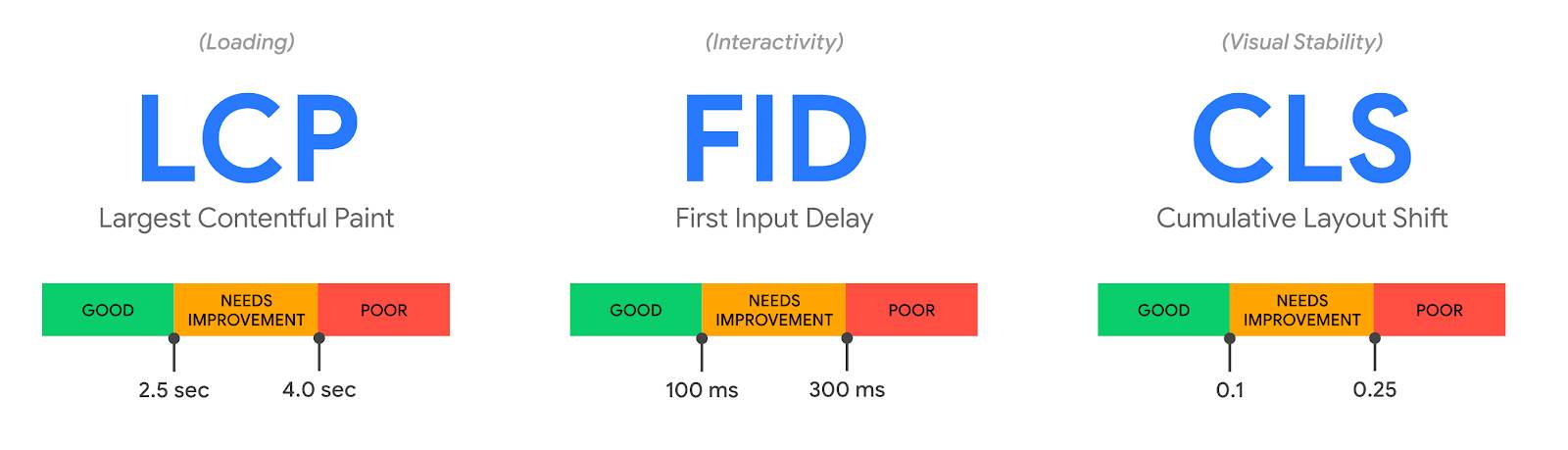 The Core Web Vitals Rating Scale – Source: https://web.dev/vitals/#core-web-vitals
The Core Web Vitals Rating Scale – Source: https://web.dev/vitals/#core-web-vitals
LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) measures how long it takes for a page to load. It is the interval between clicking a link and viewing most of the material on the screen.
The First Input Delay (FID) measures how long it takes a user to interact with your website for the first time.
CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift), sometimes known as “visual stability,” measures how steady a page is while it loads.
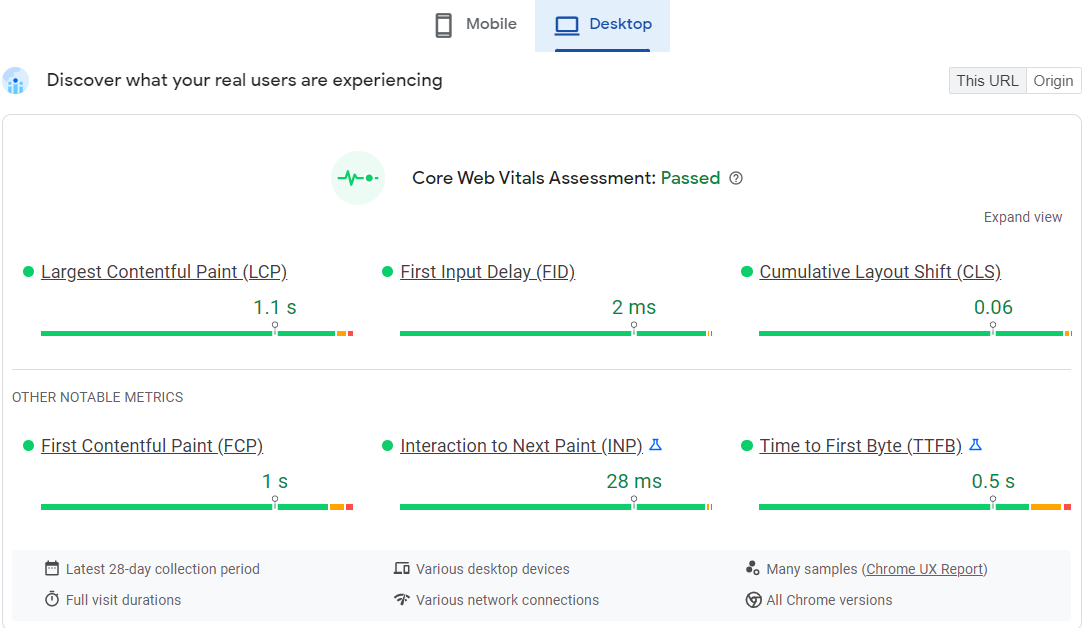
Google’s Core Web Vitals Assessment for H&M website(Desktop Version) Source: https://pagespeed.web.dev/report?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww2.hm.com%2F&formfactor=desktop
Core Web Vitals can be evaluated using the following :
How to Increase Website Performance?
Here are a few suggestions for enhancing the functionality and speed of your website to increase traffic and retain consumers.
Reduce Image Size
Huge images on your website may cause a longer loading time. Before using the images on any webpage, it is advisable to compress them to speed up this procedure.
Image compression is a technique used to reduce the size of photographs without sacrificing quality. The longer it takes for your page to load, the higher the picture file size is. Therefore, it’s crucial to compress your photographs before uploading them to your website. Here are some helpful unpaid resources:
-
TinyPNG: It reduces the size of your PNG and JPEG files using clever lossy compression algorithms.
-
ShortPixel: It is a WordPress plugin for automatically compressing images.
Minimize HTML and styles
Hypertext Markup Language, or HTML, is the foundation of almost all websites. With the help of HTML, you may structure websites with lists, headers, and other helpful text-organizing elements. Web crawlers can understand HTML effortlessly, allowing search engines to quickly update their databases with the content of your website.
You should aim to write in a way that is both concise and effective while working with HTML. Optimize your website’s code to speed up loading. Removing unnecessary formatting, comment areas, or HTML code will improve your website’s efficiency.
Lower HTTP requests
The time a webpage takes to load is directly proportional to the number of HTTP requests. The higher the number of HTTP requests, the more the webpage loading time. Larger files also take significantly longer to exchange. If your pages take longer to load, each redirect may cost you a prospective visitor. Using fewer images, text, CSS, Flash, and other elements is the easiest way to reduce your site’s HTTP requests.
Employ browser caching
Using browser caching, you may download files from your website to your hard drive and temporarily store them there. Now that those data are kept locally on your computer, subsequent page loads can happen more quickly. You must ensure that the initial page customers view loads quickly enough for them to inevitably browse the remainder of your website when they come (with even faster load times). While third-party objects like widgets or adverts only survive a day, static assets have a cached lifespan of at least a week.
Apply a CDN
A content delivery network (CDN) is a collection of geographically dispersed computers that expedites online content delivery by bringing it closer to users. The speedy delivery of static information via a CDN might be crucial to the effectiveness of your website. Content delivery networks (CDNs) store static material from your website at nodes worldwide. Thus, users that browse your website and are physically close to the CDN nodes will be able to obtain material more rapidly.
The following are a few CDN providers that can be used to improve your website’s performance:
CSS Font-Display
A great technique to improve page performance is using the CSS font-display, which regulates how font files are downloaded and shown in the browser.
The CSS font-display controls the browser’s download and display of font files, which is an excellent approach to improving page performance.
Thanks to this code, you can view the content before it has been downloaded. As a result, the visitor will get the information immediately, and the browser will gradually upload the custom font after assessing the network speed. If the speed is too sluggish and the download takes a long time, the custom font won’t be downloaded, reducing the load time.
Select the Ideal Web Hosting
Consider changing to a different hosting type if the website starts to see an increase in traffic to ensure a great user experience. Dedicated or virtual private servers (VPS) may improve speed and scalability for websites that are growing quickly or experiencing high traffic.
Optimize Database in Content Management System(CMS)
The database size increases when your CMS system has several complex plugins. This has a significant impact on how quickly your website loads. Using the right data optimization strategies may greatly enhance the functionality of your website.
Use Prefetching Techniques
Prefetching involves predicting user behavior and carrying out commands before the user does. SEO experts may better assess prospective user behavior and create cues for browsers to perform the prefetching activity. A steady user experience is ensured through the prefetching link. This prefetching should be used if you know a user will click on a specific link to get to a particular page.
Conclusion
It should be obvious that site performance and speed are essential for your website’s success after you consider all the variables mentioned above. Website speed has never been more crucial, whether you are selling products online or just sharing your personal opinions on a blog. Smart website publishers and owners are constantly seeking methods to enhance site performance.

